Why Start a Business in Dubai
Dubai’s position as a regional financial and commercial hub is supported by transparent legal structures, established trade corridors, and an economy that continues to diversify beyond traditional sectors. The regulatory environment, governed by federal law and emirate-level authorities, provides businesses with clarity regarding ownership, licensing, and operational obligations.
Benefits of Registering a Company in Dubai
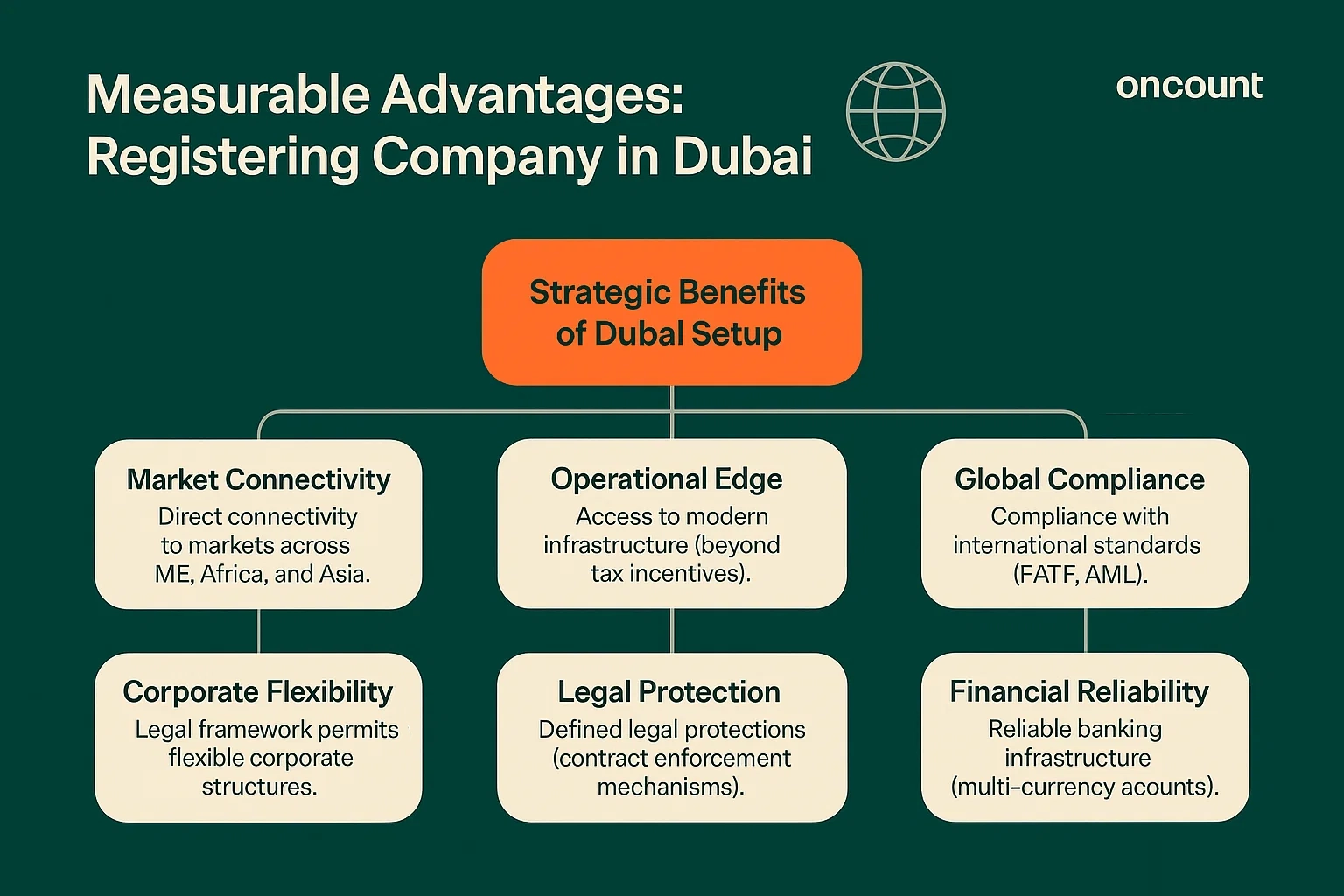
Registering a company in Dubai provides measurable advantages that extend beyond tax incentives. Entities benefit from access to modern infrastructure, streamlined incorporation procedures, and direct connectivity to markets across the Middle East, Africa, and Asia. The UAE’s legal framework permits flexible corporate structures, and entities registered within specific jurisdictions can access preferential trade agreements and bilateral investment treaties.
From a compliance perspective, the UAE has implemented frameworks aligned with international standards, including FATF guidelines on anti-money laundering (AML) and beneficial ownership disclosure. The Federal Tax Authority (FTA) oversees VAT and corporate tax obligations, ensuring transparency and predictability for business operations. Companies established under UAE law benefit from defined legal protections, including contract enforcement mechanisms and dispute resolution pathways through the courts or arbitration centers such as the Dubai International Arbitration Centre (DIAC).
For financial managers, Dubai offers reliable banking infrastructure, with both local and international institutions maintaining branch networks. Corporate banking services include multi-currency accounts, trade finance facilities, and digital payment systems that support cross-border transactions.
The UAE Economy and New Business Support
The UAE economy has demonstrated resilience through economic cycles, supported by government initiatives that encourage private sector participation and innovation. According to data published by the UAE Ministry of Economy, non-oil sectors accounted for approximately 70% of GDP in recent years, reflecting diversification into logistics, financial services, tourism, technology, and real estate.
Government authorities at both federal and emirate levels provide resources to support new business formation. The Department of Economic Development (DED) in Dubai, along with free zone authorities such as Dubai Multi Commodities Centre (DMCC) and Jebel Ali Free Zone (JAFZA), offer dedicated customer service channels, online registration portals, and guidance on licensing requirements. Regulatory bodies publish procedural updates and compliance advisories, which are accessible through official websites and electronic portals.
Business owners benefit from clear timelines for approval processes, standardized fee structures, and access to legal support services. The UAE government has also introduced measures to reduce administrative burdens, including the digitization of licensing procedures and the consolidation of regulatory touchpoints.
100% Foreign Ownership Advantage for Companies in Dubai
Legislative amendments introduced in recent years permit 100% foreign ownership of companies across most economic sectors on the UAE mainland. This regulatory shift, formalized through amendments to Federal Law No. 2 of 2015 (the Commercial Companies Law), removes the previous requirement for UAE nationals to hold majority stakes in mainland entities, with limited exceptions in sectors deemed strategic.
For foreign company representatives evaluating market entry, this development allows direct control over operations, profit distribution, and strategic decision-making without the need for local sponsors. The change applies to limited liability companies and other commercial entities, subject to sector-specific licensing conditions.
Free zone companies have historically offered 100% foreign ownership, and this remains a defining characteristic of free zone jurisdictions. Entities established in free zones continue to benefit from ownership flexibility, alongside zone-specific incentives such as exemptions from import duties and simplified customs procedures.
The regulatory framework governing foreign ownership is administered by the DED and relevant licensing authorities. Businesses must ensure compliance with sector-specific regulations, which may impose conditions on ownership structures in areas such as defense, banking, and media.
Jurisdiction Options for Business Setup
The choice of jurisdiction represents one of the most consequential decisions in the company formation process. The UAE offers three primary categories: mainland, free zone, and offshore. Each carries distinct legal, operational, and tax implications.
Mainland vs. Free Zone Companies
Registering a Company on the UAE Mainland
Mainland companies operate under the regulatory oversight of the DED and are subject to UAE federal commercial law. These entities are permitted to conduct business anywhere in the UAE, including direct engagement with government entities, local consumers, and private sector clients without geographic restrictions.
A mainland business license enables companies to participate in tenders, establish retail operations, and provide services throughout the emirate. This flexibility is particularly relevant for businesses that require physical presence in multiple locations or that serve local markets directly.
From a compliance perspective, mainland companies must adhere to UAE labor law, obtain necessary approvals from sector-specific regulatory bodies (such as the Dubai Health Authority for medical services), and maintain accounting records in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS). Corporate tax obligations, as introduced under Federal Decree-Law No. 47 of 2022, apply to taxable income exceeding AED 375,000, with a standard rate of 9%.
Mainland registration requires a physical office space, which must be verified during the licensing process. Lease agreements are submitted as part of the documentation, and inspections may be conducted depending on the nature of your business activity.
Registering a Company in a Free Zone
Free zone companies are established within designated economic zones, each governed by its own free zone authority. These authorities issue licenses, regulate business activities, and enforce zone-specific regulations. Free zones in Dubai include DMCC, JAFZA, Dubai International Financial Centre (DIFC), and Dubai Silicon Oasis, among others.
The primary advantage of free zone registration is operational flexibility. Entities benefit from simplified incorporation procedures, exemption from corporate tax for qualifying activities, and 100% repatriation of capital and profits. Free zone companies are not subject to customs duties on goods imported into or exported from the zone, which is advantageous for trading and logistics operations.
However, free zone entities face restrictions on conducting business within the UAE mainland market. To engage in mainland transactions, a free zone company typically requires a mainland distributor or service agent, unless specific exemptions apply. This limitation is a critical consideration for businesses targeting local consumers or government contracts.
Compliance requirements for free zone companies include annual license renewals, submission of financial statements, and adherence to zone-specific regulations on employment and operations. Many free zones have introduced Economic Substance Regulations (ESR), requiring entities engaged in specific activities to demonstrate adequate physical presence and decision-making within the UAE.
Offshore Companies in the UAE
Offshore companies are primarily used for holding assets, managing intellectual property, or facilitating international transactions. These entities cannot conduct business within the UAE and are typically established in jurisdictions such as Jebel Ali Offshore or RAK Offshore.
The regulatory framework for offshore companies is limited in scope. These entities are not required to file financial statements with UAE authorities, and they benefit from confidentiality provisions regarding ownership. However, offshore structures must comply with international transparency standards, including beneficial ownership disclosure under AML regulations.
Offshore companies do not receive business licenses that permit commercial operations. Their use is confined to passive activities such as holding shares, owning real estate, or managing royalties. For businesses seeking operational capacity, mainland or free zone structures are more appropriate.
Choosing the Right Free Zone for Your Company
The selection of a free zone should align with the nature of your business, the regulatory environment of the zone, and the cost structure. Each free zone authority publishes a list of permitted business activities, and licenses are issued based on these classifications.
DMCC is recognized for commodities trading, precious metals, and diamond trading. DIFC operates under a common law framework and is tailored for financial services, with its own regulatory body (the Dubai Financial Services Authority). JAFZA focuses on logistics, manufacturing, and warehousing, offering proximity to Jebel Ali Port.
When evaluating a free zone, consider the following factors:
- Permitted activities and license categories
- Cost of incorporation, including registration fees and office space
- Visa allocation based on office size
- Proximity to clients, suppliers, or transport infrastructure
- Availability of additional services such as warehousing, customs facilities, or business support
Free zone authorities provide detailed fee schedules and package options, which can be reviewed through official portals. Engaging with a corporate services provider or legal advisor familiar with zone-specific regulations can streamline the decision-making process.
Legal Structures and Company Types
The legal structure of a company determines liability exposure, ownership arrangements, governance requirements, and compliance obligations. UAE law recognizes several entity types, each suited to different operational models.
Selecting the Legal Entity for Your Company in Dubai
The choice of legal entity depends on the business model, capital requirements, and strategic objectives. For most commercial operations, the limited liability company (LLC) remains the preferred structure for mainland registration, while free zone entities often adopt simpler organizational forms.
Limited Liability Company (LLC)
An LLC is the most common legal form for mainland operations. It limits shareholder liability to the extent of their capital contribution, protecting personal assets from business liabilities. Under UAE law, an LLC may have between two and fifty shareholders, although single-shareholder LLCs are permitted under certain conditions.
The memorandum of association (MOA) governs the internal affairs of the LLC, including shareholding percentages, management authority, and profit distribution. The MOA must be notarized and filed with the DED as part of the registration process.
LLCs are subject to federal commercial law, including provisions on capital requirements (minimum paid-up capital varies by activity), governance structures, and annual reporting. Companies must appoint a manager or board of managers, whose authority is defined in the MOA.
From a tax perspective, LLCs are subject to UAE corporate tax on taxable profits. The FTA provides guidance on allowable deductions, transfer pricing requirements, and documentation standards. Financial statements must be prepared in accordance with IFRS and retained for audit purposes.
Branch Office or Representative Office
Foreign companies with established operations in other jurisdictions may open a branch office or representative office in Dubai. A branch office is permitted to engage in commercial activities and generate revenue, while a representative office is limited to marketing, liaison, and business development functions.
Branch registration requires parent company documentation, including a certificate of incorporation, board resolution authorizing the branch, and audited financial statements. The branch operates under the parent company’s legal identity and does not constitute a separate legal entity.
Representative offices do not issue commercial invoices and cannot enter into contracts on behalf of the parent company. They serve as a point of contact for clients and partners, facilitating market research and relationship development.
Legal Forms for Free Zone Companies
Free zone companies typically adopt one of three structures: Free Zone Establishment (FZE), Free Zone Company (FZC), or branch of a foreign company.
An FZE is a single-shareholder entity, suitable for sole proprietorships or wholly owned subsidiaries. An FZC permits multiple shareholders, with a minimum of two required. Both structures offer limited liability and are governed by the regulations of the respective free zone authority.
Branch offices of foreign companies may operate within free zones, provided the parent entity meets the authority’s registration requirements. This structure allows international firms to establish a local presence without creating a separate legal entity.
Free zone legal structures are defined by the regulations of each zone, which may impose specific governance or reporting requirements. Entities should review the applicable rules before finalizing their legal form.
Step-by-Step Company Registration Process
The process of company registration in Dubai follows a structured sequence, with variations depending on jurisdiction and business type. Understanding each stage ensures compliance and reduces the risk of delays.
Steps to Establish Your Company in Dubai
Choose Your Business Activity and Type of Company
The first step involves defining the scope of your business operations. The UAE categorizes business activities into broad classifications: commercial, professional, industrial, and tourism-related. Each activity is governed by specific licensing requirements and may require approvals from regulatory bodies.
For example, healthcare services require licensing from the Dubai Health Authority, while educational services fall under the Knowledge and Human Development Authority (KHDA). Food and beverage operations require health and safety permits from Dubai Municipality.
Your chosen business activity determines the type of license required and influences the selection of jurisdiction. Some activities are restricted to mainland operations, while others may only be conducted in specific free zones.
Determine Your Company’s Legal Structure
Once the business activity is defined, select the appropriate legal structure. Consider factors such as liability exposure, ownership preferences, and long-term strategic goals. The legal structure impacts capital requirements, governance obligations, and tax treatment.
Consulting with a legal advisor or corporate services provider can clarify the implications of each structure and ensure alignment with your business objectives.
Register Your Trade Name
The trade name must be unique, comply with UAE naming conventions, and reflect the nature of your business. Names cannot include words that are offensive, misleading, or reserved for government use. The DED provides an online search tool to verify name availability.
For mainland companies, the trade name must be registered with the DED and approved before proceeding with licensing. Free zone authorities have their own naming guidelines, which are typically more flexible than mainland requirements.
Obtaining Initial Approval and a Business License
Prepare Required Documents
The documentation package varies by jurisdiction and entity type, but typically includes:
- Passport copies of shareholders and managers
- Proof of address for shareholders
- Memorandum of association (for LLCs)
- Business plan outlining objectives and projected activities
- No-objection certificate (NOC) from current sponsor, if applicable
- Office lease agreement or Ejari registration
For free zone registration, the authority may require additional documents, such as a bank reference letter or professional credentials for licensed activities.
All documents must be submitted in the format specified by the licensing authority. Some jurisdictions require notarization, legalization, or attestation by UAE consulates abroad.
Online Company Registration in Dubai
Many authorities have introduced online platforms to streamline the registration process. The DED’s online portal, Invest in Dubai, allows applicants to submit forms, upload documents, and track application status electronically. Similarly, free zone authorities offer digital registration systems that reduce processing time.
Online registration typically involves creating an account, selecting the business activity, entering shareholder details, and uploading required documents. Payments for registration fees and licensing costs can be processed through the portal.
Processing times vary but generally range from a few days to several weeks, depending on the complexity of the application and the need for external approvals.
Types of Business Licenses
The type of license issued determines the scope of permissible activities and the regulatory obligations applicable to your company. The UAE requires a business license for all commercial operations, and licenses are activity-specific.
The Different Types of Business Licenses
Commercial License
A commercial license is issued for trading activities, including import, export, wholesale, and retail operations. Entities engaged in the sale of goods, whether locally or internationally, require a commercial license.
The scope of a commercial license is defined by the specific goods listed in the license. Adding or modifying product categories requires amending the license, which involves additional fees and approvals.
Commercial licenses are subject to compliance with customs regulations, consumer protection laws, and sector-specific requirements. For example, trading in pharmaceuticals requires approval from the Ministry of Health, while foodstuffs require certification from Dubai Municipality.
Professional License
Professional licenses are issued for service-based businesses, including consultancy, legal services, accounting, engineering, and creative industries. These licenses are typically issued to individuals or companies providing expertise-based services.
Professional licenses may require the license holder to possess specific qualifications or certifications. For instance, auditing firms must be registered with the UAE Ministry of Economy, and legal consultancies require advocates licensed by the UAE courts.
Professional licenses do not permit trading activities. Businesses that provide both services and goods may require a dual license or a commercial license with an expanded scope.
Industrial License
Industrial licenses are issued for manufacturing, processing, or assembly operations. These licenses are typically issued by free zone authorities or the DED, depending on the location of the facility.
Industrial activities require compliance with environmental regulations, occupational health and safety standards, and zoning requirements. Companies must obtain approvals from Dubai Municipality or relevant authorities before commencing operations.
Industrial licenses may include sub-categories for light manufacturing, heavy industry, or food processing. The specific category determines the facility requirements and inspection procedures.
How to Get a Business License for Your New Business
Obtaining a business license involves submitting an application to the relevant authority, providing supporting documentation, and paying the prescribed fees. The process begins after initial approval of the company name and legal structure.
For mainland companies, the DED reviews the application and may request additional information or external approvals. Once all requirements are satisfied, the license is issued electronically and can be downloaded from the applicant’s account.
Free zone authorities follow a similar process, with licenses typically issued more quickly due to streamlined procedures. Some zones offer express services for an additional fee.
Business licenses are valid for one year and must be renewed annually. Renewal requires submission of updated documents, including a valid lease agreement and proof of compliance with any sector-specific obligations.
Required Documents for UAE Company Registration
Accurate and complete documentation is essential for a smooth registration process. Missing or incorrect documents are the most common cause of delays.
Document Checklist to Start Your Business in Dubai
The standard document checklist includes:
- Passport copies of all shareholders and directors (attested if required)
- Recent passport-sized photographs
- Proof of residential address (utility bill or tenancy contract)
- Memorandum of association or articles of association
- Business plan (required by some authorities)
- No-objection certificate from current sponsor (for UAE residents)
- Office lease agreement or tenancy contract
- Ejari registration (for mainland companies)
- Bank reference letter (required by some free zones)
- Professional certifications or degrees (for professional licenses)
For branch offices, additional documents include the parent company’s certificate of incorporation, board resolution, and audited financial statements for the past two years.
All documents must be clear, legible, and submitted in the format specified by the authority. Translation into Arabic may be required for certain documents, particularly for notarization purposes.
Opening a Corporate Bank Account
Once the business license is issued, the next priority is establishing banking facilities. Opening a corporate bank account in Dubai requires the company’s registration documents, licenses, and identification for authorized signatories.
Banks conduct due diligence in accordance with UAE Central Bank regulations and AML requirements. The bank will request:
- Trade license and memorandum of association
- Certificate of incorporation
- Passport copies of shareholders and authorized signatories
- Proof of business address
- Description of business activities and anticipated transaction volumes
- Source of funds declaration
Account opening can take several weeks, as banks verify documentation and assess risk profiles. Having a well-prepared business plan and clear financial projections can facilitate the process.
Some free zones have partnerships with specific banks, which may expedite account opening for companies registered within those zones.
Cost of Company Formation
The financial commitment required to start your company in Dubai varies significantly based on jurisdiction, business activity, and the legal structure selected.
Expenses for Company Registration in Dubai
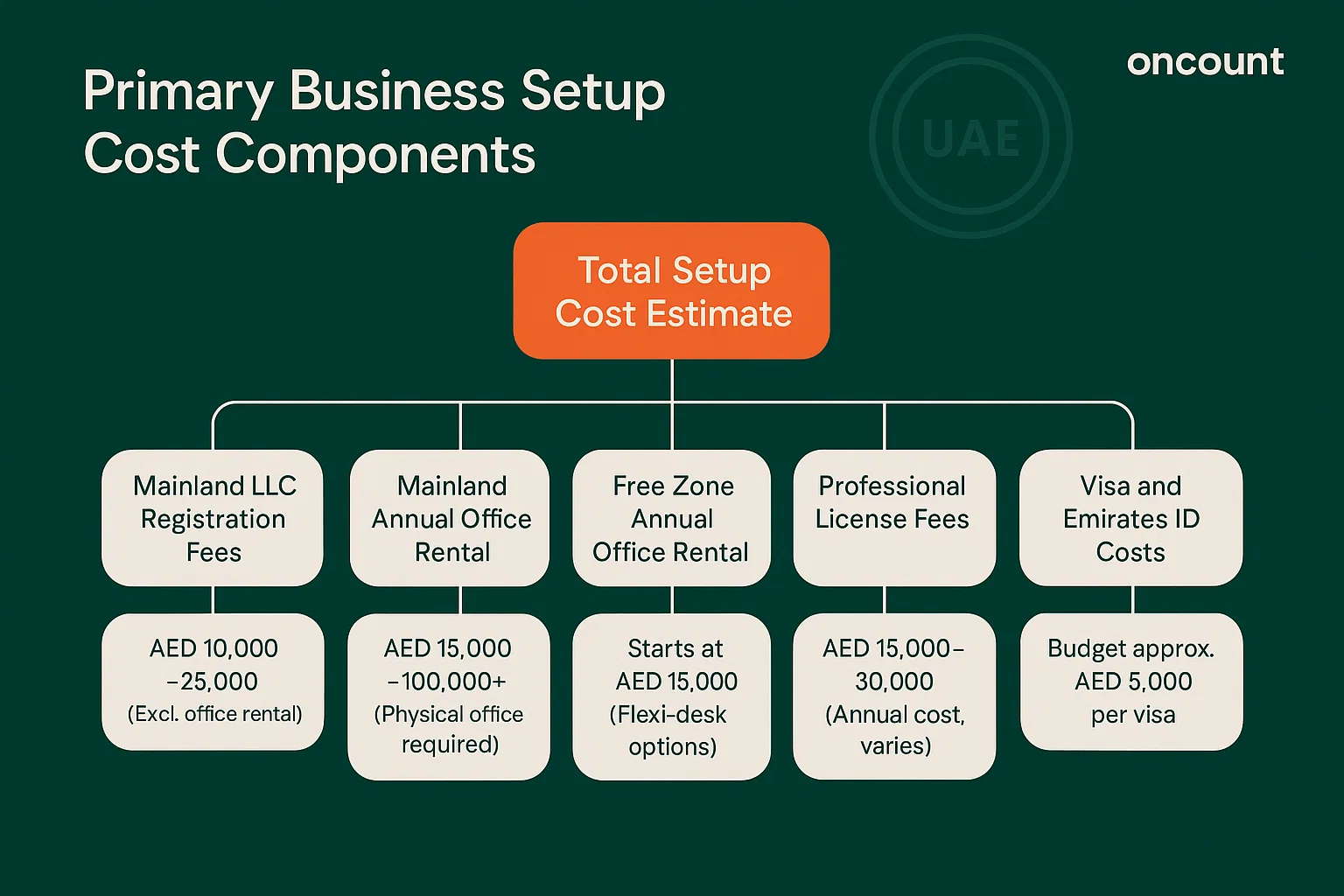
The primary cost components include:
- Registration fees: Payable to the DED or free zone authority, these fees vary by entity type and zone. Mainland LLC registration fees typically range from AED 10,000 to AED 25,000, excluding office rental.
- Office rental: Mainland companies require a physical office, with annual costs ranging from AED 15,000 for a basic desk space to over AED 100,000 for larger facilities. Free zones offer flexible office solutions, including flexi-desk options starting at approximately AED 15,000 annually.
- License fees: Annual licensing costs vary by activity and jurisdiction. Professional licenses generally range from AED 15,000 to AED 30,000, while commercial and industrial licenses may be higher.
- Visa costs: Investor and employee visa fees include Emirates ID issuance, medical examinations, and immigration processing. Budget approximately AED 5,000 per visa, including all associated costs.
- Document attestation: Legalization and notarization of foreign documents may cost between AED 1,000 and AED 5,000, depending on the volume and origin of documents.
Additional costs may include legal advisory fees, accounting services, and initial compliance filings.
Cost Comparison: Mainland vs. Free Zone Setup
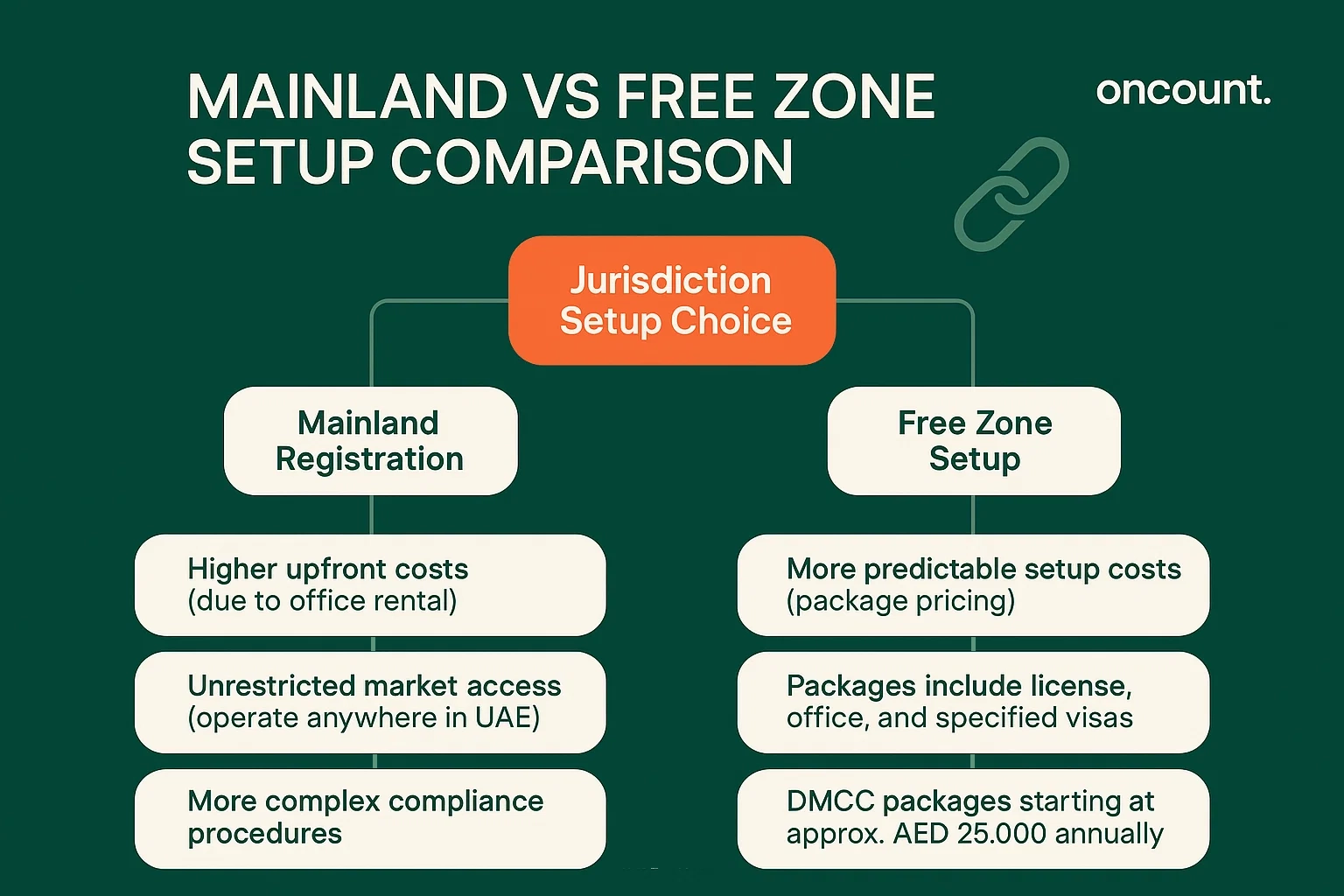
Mainland registration typically involves higher upfront costs due to office rental requirements and more complex compliance procedures. However, mainland businesses benefit from unrestricted market access and the ability to operate anywhere in the UAE.
Free zone setup costs are often more predictable, with package pricing offered by many authorities. Free zone packages may include the license, office space, and a specified number of visas. For example, DMCC offers packages starting at approximately AED 25,000 annually, including flexi-desk access and one visa.
When comparing costs, consider the long-term implications of market access restrictions for free zone entities and the need for local service agents when serving mainland clients.
Hidden Fees and Tax Requirements
Businesses should account for ongoing compliance costs, including:
- Audit fees: Companies meeting certain thresholds must conduct annual audits. Fees range from AED 10,000 to AED 50,000, depending on transaction volume and complexity.
- VAT registration and filing: Entities exceeding the mandatory registration threshold of AED 375,000 in taxable supplies must register for VAT and file quarterly returns. Accounting fees for VAT compliance typically range from AED 3,000 to AED 10,000 annually.
- Corporate tax compliance: With the introduction of UAE corporate tax, businesses must maintain detailed records and file annual tax returns. Tax advisory and filing costs vary based on the complexity of operations.
- ESR filing: Entities subject to Economic Substance Regulations must submit annual notifications and reports. Non-compliance may result in penalties.
Budgeting for these ongoing obligations ensures sustainable business operations and avoids unexpected financial strain.
Visa and Immigration for Business Owners
Securing residency visas is a critical post-registration step for business owners and key personnel. The UAE visa system links residency rights to employment or business ownership.
Investor and Partner Visa Requirements
Investors and shareholders holding a qualifying stake in a UAE company are eligible for investor visas. The specific requirements depend on the jurisdiction and the company’s capital structure.
For mainland LLCs, shareholders typically qualify for investor visas regardless of shareholding percentage, provided the company is fully licensed. Free zone companies allocate visas based on the type of license and office space. A flexi-desk license may permit one or two visas, while larger office spaces allow additional allocations.
Investor visas are valid for two or three years, depending on the category. The UAE has introduced long-term residency options, including five- and ten-year visas for investors meeting capital thresholds or other criteria.
The Visa Process for a Business Owner
The visa application process involves several stages:
- Entry permit issuance: The company sponsors the entry permit, which allows the applicant to enter the UAE for medical testing and Emirates ID registration.
- Medical examination: Required for all visa applicants, conducted at approved centers. Results are typically available within 48 hours.
- Emirates ID application: Biometric data is collected, and the application is submitted to the Federal Authority for Identity and Citizenship.
- Visa stamping: Once medical clearance and Emirates ID approval are obtained, the visa is stamped in the passport.
The entire process typically takes two to four weeks. Delays can occur if documentation is incomplete or if additional approvals are required.
Family Sponsorship Options
Business owners holding investor visas may sponsor family members, including spouses, children, and, in some cases, parents. Sponsorship requires proof of income or salary (minimum thresholds apply), suitable accommodation, and completed medical examinations for all sponsored individuals.
Family sponsorship enhances the attractiveness of UAE residency, allowing dependents to access education, healthcare, and employment opportunities within the country. Sponsored family members receive residence visas with the same validity period as the sponsor’s visa.






