Who Is Required to File VAT Returns in the UAE?
Registration and return filing obligations apply to specific categories of businesses based on annual turnover and operational characteristics. According to FTA guidance, those with annual taxable supplies exceeding AED 375,000 must register, while entities with turnovers between AED 187,500 and AED 375,000 may register voluntarily to recover input paid on business expenses.

Once registered, all entities must file periodic returns even if no transactions occurred during the reporting cycle. This includes businesses engaged in international trade, those subject to reverse charge mechanisms, and entities operating in both mainland and free zone jurisdictions. Free zone companies often face additional considerations, especially when transacting with mainland UAE entities or engaging in cross-border commerce.
Filing Frequency and Deadlines
The frequency with which businesses are required to file vat returns depends on their annual turnover threshold. Businesses with annual taxable supplies below AED 150 million submit quarterly returns, while those exceeding this threshold must file monthly returns. The FTA may assign different tax periods to specific business types based on operational characteristics or industry requirements.
Critical Filing Deadlines
Filing Value-added tax returns and making payments must occur within 28 days following the end of each return period. For example, a business with a January–March tax period faces an April 28 filing deadline. When filing dates for Value-added tax returns fall on weekends or public holidays, the deadline automatically extends to the first subsequent business day. This extension applies to both the submission of returns and the payment of any net tax due.
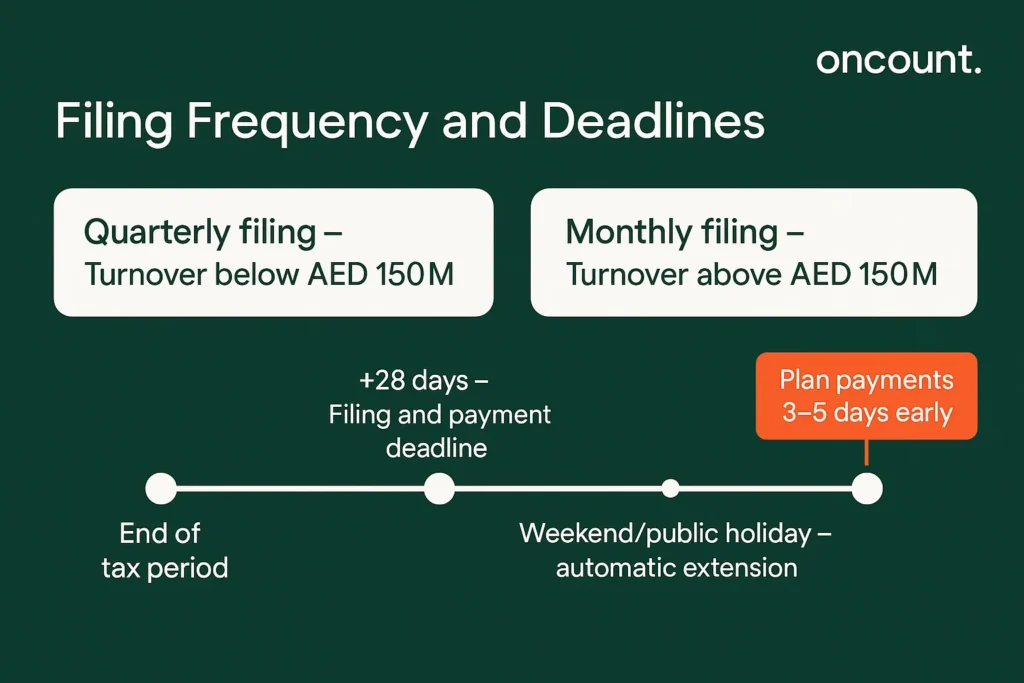
In practice, businesses should account for payment processing times when planning their compliance timeline. Bank transfers typically require two to three business days to complete, making it prudent to initiate payments several days before the filing deadline to ensure timely receipt by the FTA.
Documents Required for VAT Return Filing
Before initiating the vat return filing process, businesses must compile comprehensive documentation to support their submissions. The documents required for vat return filing include:
- Tax Registration Certificate (TRC): Issued by the FTA upon successful vat registration, confirming the business’s registered status
- Trade License: Proof of legal business registration with the relevant UAE authority
- Tax Invoices: Complete sales invoices containing supplier and customer information, vat amounts, and transaction details
- Purchase Invoices: Documentation of vat paid to suppliers on business expenses
- Financial Records: Profit and loss statements, balance sheets, and bank statements covering the relevant return period
- Import/Export Declarations: Required documentation for international trade transactions
- Credit and Debit Notes: Records of adjustments to previously issued invoices
- Previous VAT Returns: Historical submissions to ensure consistency and accuracy
Maintaining organized, accessible records throughout the tax period simplifies the vat return filing in uae and reduces the risk of errors or omissions that could trigger FTA scrutiny.
Accessing the VAT Return Form Through the FTA Portal
Businesses must file vat returns electronically through the FTA’s online platform, known as the EMARATAX portal. To access the vat return form, authorized representatives should navigate to www.tax.gov.ae and authenticate using registered credentials or UAE Pass for enhanced security.
Once logged into the fta portal, users should:
- Select the ‘VAT’ section from the main navigation menu
- Click ‘My Filings’ followed by ‘View All’
- Identify the unfiled return period, which appears without a VAT return period reference number
- Click ‘File’ for the corresponding tax period to begin the submission process
The system prompts users to confirm they have reviewed filing instructions and guidelines before proceeding. This acknowledgment ensures businesses understand their obligations and the accuracy requirements for submitted information.
Completing Form 201: Section-by-Section Guide
The return form, known as Form 201, comprises seven distinct sections that capture comprehensive information about a business’s Value-added tax activities during the tax period. Understanding how to file a Value-added tax return requires familiarity with each section’s requirements and the data needed for accurate completion.

Section 1: Taxable Person Details
This section contains details pre-populated from the vat registration records, including the Tax Registration Number (TRN), business name in English and Arabic, and registered business address. Businesses should verify this information remains current and accurate.
Section 2: VAT Return Period Information
Section 2 automatically indicates the vat return period under review, including the tax year end date, filing deadline, and the vat return period reference number. This reference number becomes essential for tracking submissions and correspondence with the FTA.
Section 3: VAT on Sales and Other Outputs
This section requires businesses to report all sales and supplies made during the return period, categorized by their VAT treatment. The appropriate boxes of the vat return must be completed to reflect:
- Standard-rated supplies (5%): Domestic sales subject to the standard UAE VAT rate
- Zero-rated supplies: Exports, qualifying education services, healthcare provisions, and international transport
- Exempt supplies: Financial services, residential property transactions, and bare land sales
- Reverse charge transactions: Imported goods or services where the recipient accounts for VAT
- Adjustments: Discounts, bad debts, credit notes, or other modifications to previously reported amounts
The sum of the output vat from these categories represents the total vat collected from customers during the tax period.
Section 4: VAT on Expenses and Other Inputs
Businesses must report all purchases and expenses where tax paid to suppliers can be recovered as input Value-added tax. This includes:
- Standard-rated purchases subject to 5% Value-added tax
- Reverse charge mechanism purchases where the business self-accounts for tax
- Imports from GCC member states and non-GCC countries
- Total recoverable tax amount eligible for offset against output tax
Accurate recording of input tax is crucial for determining the correct net payable or refundable amount.
Section 5: Net VAT Due Calculation
This critical section calculates the business’s Value-added tax liability for the tax period. The boxes of the return form include:
- Box 12: Total output tax collected on sales and supplies
- Box 13: Total input tax paid on purchases and expenses
- Box 14: Net tax due, calculated as output tax minus input tax
When output and input tax are compared, if the output tax that is due exceeds recoverable input amounts, the business must pay the difference. Conversely, if input exceeds output, the business may claim a refund or carry the credit forward to subsequent periods. This net payable or refundable amount represents the total tax due for the period.
Section 6: Additional Reporting Requirements
Businesses must indicate whether they utilized the Profit Margin Scheme during the tax period. Most standard businesses select ‘No’ and proceed to the final section.
Section 7: Declaration and Authorized Signatory
The final section requires entry of the authorized signatory’s details and confirmation that all information provided is accurate and complete. This declaration carries legal weight, making accuracy and thoroughness paramount when businesses file the vat return.
VAT Filing Deadlines and Penalties: A Quick Reference
Understanding the penalty structure for non-compliance is essential for all businesses engaged in return filing in the uae. The table below summarizes key deadlines and associated penalties:
| Violation Type | Penalty Amount | Application Timeline | Additional Notes |
| Late Filing – First Offense | AED 1,000 | Immediately after deadline | Applies regardless of tax due |
| Late Filing – Repeat Offense | AED 2,000 | Within 24 months of previous violation | Escalates with frequency |
| Late Payment – Initial Penalty | 2% of unpaid VAT | Immediately after deadline | Applied to total outstanding amount |
| Late Payment – Monthly Penalty | 4% per month | Each month payment remains outstanding | Compounds until paid |
| Maximum Late Payment Penalty | 300% of unpaid VAT | Cumulative cap | Can reach three times original liability |
| Late Registration | AED 10,000 | Exceeding threshold without registration within 30 days | Applies to mandatory registration only |
This penalty framework underscores the importance of timely submission and payment of the due tax for the period to avoid escalating financial consequences.
Review, Submission, and Payment Procedures
Before submitting their returns, businesses should carefully review to ensure:
- All calculations reflect accurate amounts and applicable rates
- Figures match supporting documentation and financial records
- No duplicate entries or missing transactions exist
- All required fields are completed correctly
After submission, the FTA portal issues a confirmation email with a receipt documenting the filing, which should be retained for compliance purposes.
When the new return shows an amount payable, businesses must complete payment through the FTA portal using approved electronic methods such as e-Dirham cards, bank transfers, or other digital channels. The total amount due must be settled within the same 28-day deadline that applies to return filing.
VAT Filing Deadlines in UAE: Compliance Imperatives
Understanding and adhering to vat filing deadlines in uae is non-negotiable for maintaining good standing with the Federal Tax Authority. The consequences of late submission or payment can be substantial and escalate with repeated violations.
Late Filing Penalties
Businesses that fail to submit vat returns on time face immediate financial penalties:
- AED 1,000 for the first violation
- AED 2,000 for repeated violations occurring within 24 months
Late Payment Penalties
The penalty structure for late payment of the vat amount due is more severe and accumulates over time:
- 2% of the unpaid VAT assessed immediately after the filing deadline passes
- Additional 4% penalty applied monthly for each month the balance remains unpaid
- Maximum aggregate penalty capped at 300% of the total unpaid VAT
For instance, a business owing AED 50,000 that pays seven days late incurs an immediate penalty of AED 1,000 (2% of AED 50,000), with additional monthly penalties accruing until full payment is received.
Late Registration Penalties
Businesses exceeding the AED 375,000 annual turnover threshold face a penalty of AED 10,000 if they fail to register for vat within 30 days of crossing the mandatory registration threshold.
Important Filing Dates for VAT Returns: Planning for Compliance
Effective compliance requires proactive planning around important filing dates for vat returns. Businesses should establish internal deadlines that allow adequate time for data compilation, review, and submission well before the FTA’s statutory deadline.
Best practices include:
- Implementing monthly or quarterly closing procedures that align with the return period
- Designating specific team members responsible for gathering and verifying vat-related documentation
- Scheduling internal review meetings at least one week before the filing deadline
- Initiating payment processing at least three to five business days before the due date
- Maintaining a compliance calendar that tracks all applicable vat filing deadlines in uae
Even when no business transactions occur during a tax period, businesses are required to file vat returns showing nil activity. Failure to submit a nil return carries the same penalties as failing to submit an active return.
Regulations and Record Retention Requirements
UAE Value-added tax regulations mandate that registered businesses maintain comprehensive records of all tax-related transactions and filings for a minimum of five years from the end of the relevant tax period. These records must be accessible for FTA inspection and include:
- Original VAT returns submitted to the FTA
- Payment confirmation receipts and bank statements
- Tax invoices for sales and purchases
- Import and export documentation
- Credit and debit notes
- Accounting records and financial statements
In practice, businesses should implement robust document management systems that facilitate easy retrieval of historical information when responding to FTA inquiries or conducting internal audits.
Special Considerations for UAE Businesses
Free Zone vs. Mainland Operations
Free zone entities often navigate distinct compliance requirements when conducting transactions with mainland businesses or international parties. While designated zone transactions may qualify for zero-rating, sales to mainland UAE customers typically attract the standard 5% VAT rate. Understanding these nuances is essential when businesses must file vat returns that accurately reflect their transaction mix.
Reverse Charge Mechanism
When UAE businesses import services from foreign suppliers, they typically account for VAT using the reverse charge mechanism. This requires the recipient to self-assess both output vat (as if making a supply) and input vat (as if receiving a supply), with the net effect often being neutral for fully taxable businesses. However, accurate reporting in the appropriate boxes of the vat return remains mandatory.
Real Estate Sector Considerations
Real estate businesses face particular complexity when filing vat returns in uae due to varying treatments for commercial versus residential properties, land sales, and the first supply rules. Commercial property transactions generally attract standard-rate VAT, while residential properties benefit from exempt or zero-rated treatment depending on specific circumstances.
Engaging Professional Support for VAT Filing in the UAE
Given the complexity of return filing in the UAE and the significant penalties for non-compliance, many businesses engage qualified advisors or certified agents specializing in UAE fiscal regulations. Professional support can provide:
- Expert interpretation of complex transaction treatment scenarios
- Systematic reconciliation of amounts collected and paid
- Proactive identification of optimization opportunities
- Representation during FTA audits or inquiries
- Training for internal finance teams on procedural requirements
When selecting advisors, businesses should verify credentials, UAE-specific experience, and familiarity with both Federal Tax Authority procedures and industry practices relevant to their operations.
Ensuring Accurate VAT Return Filing: Best Practices
To learn how to file vat returns effectively and maintain consistent compliance, businesses in the uae should adopt these proven practices:
Implement Robust Accounting Systems
Modern accounting software with Value-added tax–specific modules can automate much of the data compilation required to file returns in the UAE. These systems should track both output tax and input tax in real time, categorize transactions according to their Value-added tax treatment, and generate reports that align with Form 201 requirements.
Conduct Regular Reconciliations
Monthly reconciliation of VAT accounts, even when businesses are required to file quarterly returns, helps identify discrepancies early and ensures the vat return filing process proceeds smoothly when deadlines approach.
Document Decision-Making
When complex transactions require judgment about appropriate VAT treatment, businesses should document their reasoning with reference to specific FTA guidance or relevant vat regulations. This documentation proves valuable if the FTA requests clarification during a review.
Stay Current with Regulatory Updates
The Federal Tax Authority periodically issues updates, clarifications, and amendments to regulatory guidelines. Businesses must stay informed about any changes that could affect how returns are filed or how the net amount due is calculated for future periods.
Utilize FTA Resources
The FTA provides various resources to help businesses understand their obligations and learn how to file accurate vat returns electronically. These include user guides, video tutorials, public clarifications, and a dedicated helpline for technical questions about the fta portal or specific vat return filing in uae procedures.
Conclusion: Maintaining VAT Compliance in the UAE
Filing vat returns and making payments on time represents a fundamental compliance obligation for all registered businesses in the uae. The process requires systematic attention to detail, comprehensive documentation, and thorough understanding of how different transaction types affect the total tax due calculation.
By establishing robust internal processes, leveraging appropriate technology solutions, and engaging professional expertise when necessary, businesses can efficiently manage their vat return filing obligations while minimizing compliance risks. The guide for businesses presented here provides the foundation for understanding required procedures, but successful long-term compliance requires ongoing commitment to accuracy, timeliness, and awareness of evolving vat regulations.
As the UAE continues to refine its tax framework and the Federal Tax Authority enhances its enforcement capabilities, businesses that prioritize vat compliance position themselves for sustainable success in the UAE market. Whether operating in Dubai’s dynamic business environment or across other emirates, maintaining accurate vat returns ensures businesses meet their regulatory obligations while optimizing their tax position within the bounds of applicable law.




