Legal Foundation and Framework of UAE Contract Law
The UAE civil code represents a unique blend of legal traditions, incorporating Islamic Sharia principles alongside modern civil law concepts derived from Egyptian and French legal systems. Article 1 of the Civil Code establishes that when specific statutory provisions are absent, UAE courts shall adjudicate according to Islamic Sharia, particularly referencing the schools of Imam Malik and Imam Ahmad Ben Hanbal.
This mixed legal system creates a robust framework that balances traditional Islamic jurisprudence with contemporary commercial needs. The federal law applies uniformly across the United Arab Emirates, though specialized jurisdictions like the Dubai International Financial Centre operate under modified regulations that incorporate elements of English common law for specific commercial transactions.
Key Elements of Contract Law in the UAE
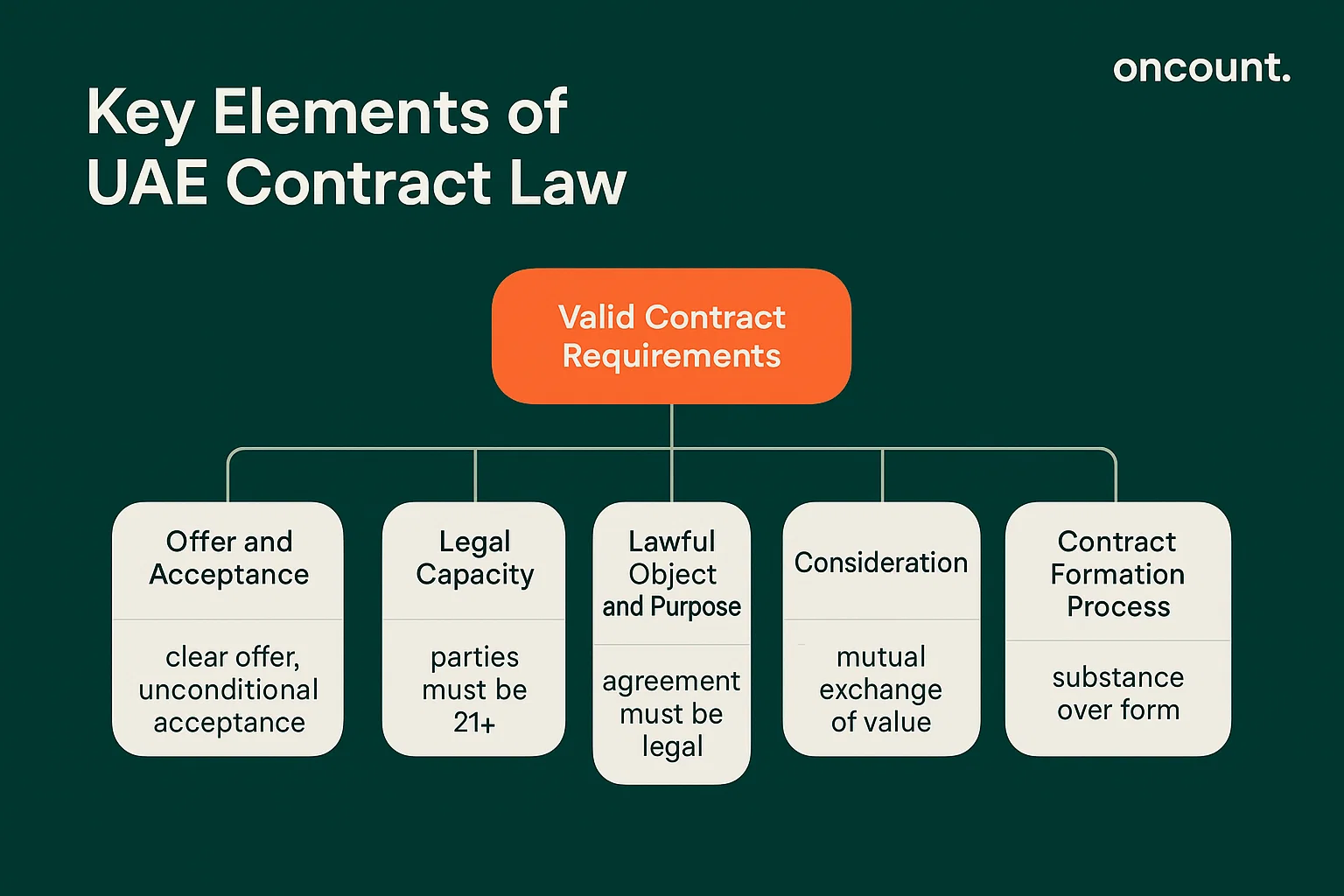
Under the UAE Civil Code, every valid contract must satisfy four fundamental requirements as outlined in Articles 129–131.:
Offer and Acceptance Requirements
A contract is formed when a clear offer meets unconditional acceptance. The offer must specify essential terms including subject matter, price, and performance timelines. The Civil Transactions Law requires that acceptance correspond exactly to the offer’s terms – any modification constitutes a counter-offer requiring fresh acceptance.
Legal Capacity of Contracting Parties
Both parties must possess the legal capacity to enter into contractual obligations. The UAE legal system establishes that individuals aged 21 or older possess full contractual capacity unless deemed incapable due to mental incompetence. Contracts entered by minors or those lacking mental capacity may be rendered invalid.
Lawful Object and Purpose
The agreement’s subject matter must be possible, clearly specified, and legally permissible under UAE law. Any contract violating public policy, morality, or existing laws and regulations becomes void ab initio.
Consideration and Mutual Exchange
While not explicitly defined as in common law systems, the UAE civil code requires an exchange of value between contracting parties. This consideration may involve monetary payment, goods, services, or any other lawful benefit.
Contract Formation Process Under UAE Law
Article 125 defines a contract as “the meeting of an offer issued by one of the contracting parties with the acceptance made by the other party and their concordance in such a manner as to produce their effect on the object of the contract.” Expression of contractual intent may occur through:
- Written documentation
- Verbal agreement
- Customary signs or conduct
- Electronic communication methods
The law emphasizes substance over form, recognizing that parties may demonstrate mutual consent through various means of communication.
Fundamental Principles Governing UAE Contracts
Good Faith Obligations
The principle of good faith stands as the cornerstone of UAE contract law. Article 246 explicitly mandates that “contracts must be performed in good faith,” establishing an obligation that extends throughout the entire contractual relationship. This requirement encompasses:
- Honest and transparent dealing
- Full disclosure of material information
- Respect for legitimate expectations
- Avoidance of rights abuse
- Cooperative performance attitudes
Dubai courts consistently emphasize that good faith constitutes an essential element of every contract, with the Dubai Court of Cassation ruling that this principle must be observed by all parties involved.
Freedom to Contract
Article 257 protects parties’ autonomy in determining contractual terms, subject to limitations imposed by law, public policy, and good faith requirements. This freedom allows businesses to structure agreements according to their specific needs while ensuring compliance with mandatory legal provisions.
Binding Nature of Contractual Obligations
Once validly formed, contracts create binding obligations under Article 267. Valid contracts cannot be unilaterally terminated except through:
- Mutual consent of both parties
- Court order based on legal grounds
- Specific legal provisions allowing termination
Types of Contracts in the UAE Legal System
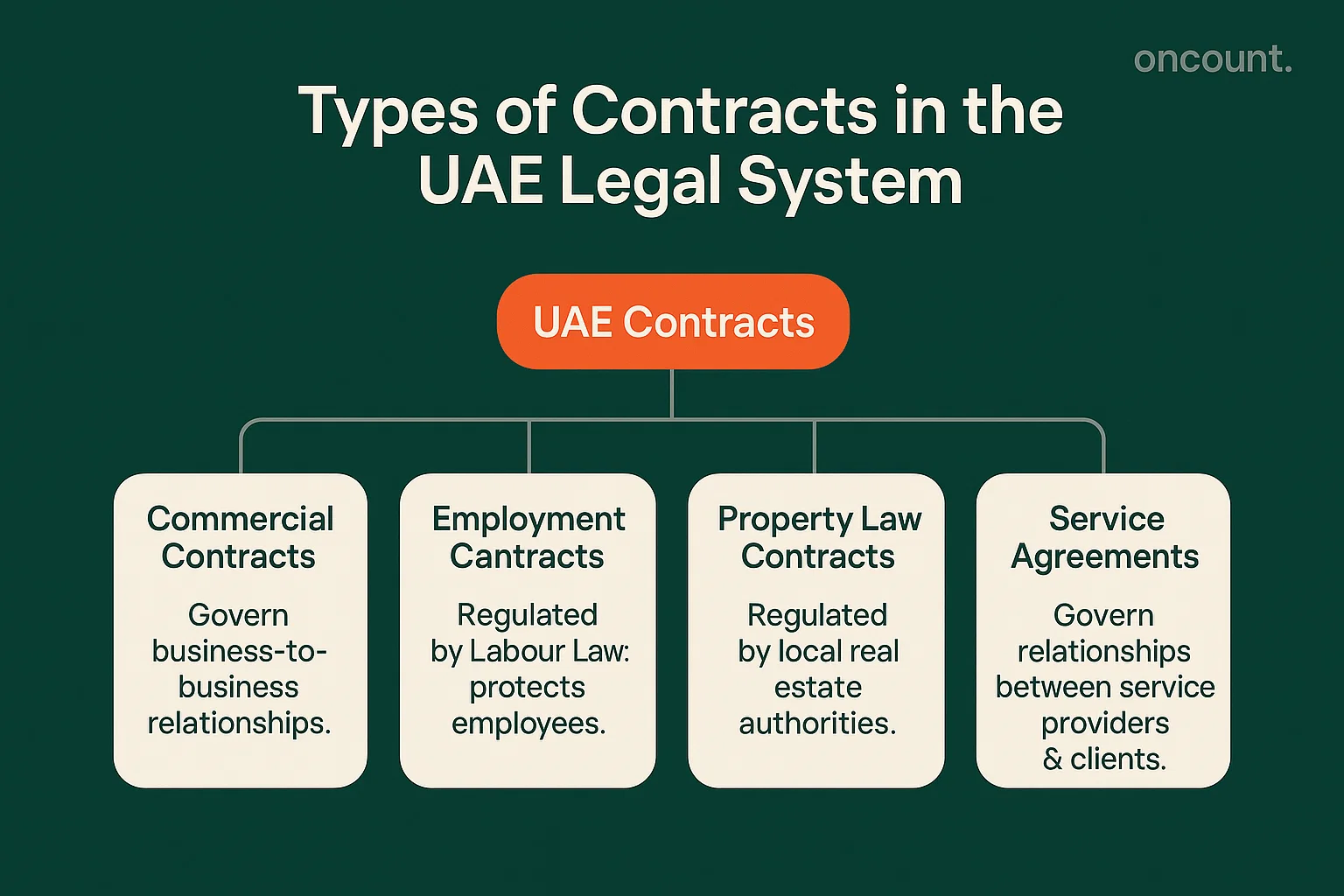
The UAE civil code recognizes numerous contract types, each governed by specific provisions:
Commercial Contracts
These agreements govern business-to-business relationships, including supply agreements, distribution contracts, and joint venture arrangements. Commercial contracts typically involve sophisticated terms addressing force majeure, governing law, and dispute resolution mechanisms.
Employment Contracts
Employment contracts, regulated by both the Civil Transactions Law and the updated UAE Labour Law (Federal Decree-Law No. 33 of 2021), establish protections for employees while ensuring clarity in employer-employee obligations. For further reference and official text, consult MoHRE’s laws and regulations portal with downloadable PDFs of the Labour Law.
Property Law Contracts
Real estate transactions fall under specialized provisions addressing property transfer, lease agreements, and development contracts. These contracts must comply with additional requirements established by local real estate regulatory authorities.
Service Agreements
Professional service contracts govern relationships between service providers and clients, with specific attention to performance standards and liability limitations.
Contract Interpretation Under UAE Law
Article 258 establishes the fundamental principle that “the criterion in the construction of contracts is intentions and meanings and not words and forms.” UAE courts interpret agreements by examining:
- Express contractual language
- Parties’ demonstrated intentions
- Surrounding circumstances at formation
- Applicable commercial customs
- Good faith principles
When contract terms are clear and unambiguous, courts must respect the plain meaning. However, vague or unclear provisions require deeper analysis of the parties’ actual intentions and commercial context.
Breach of Contract and Available Remedies
Elements of Contractual Breach
Article 124 identifies contracts as primary sources of personal obligations. Breach of contract occurs when three elements coincide:
- Fault or breach by one contracting party
- Proven damages suffered by the affected party
- Direct causal relationship between breach and damages
Remedies for Contract Breach
| Remedy Type | Article Reference | Application | Limitations |
| Specific Performance | Article 272 | When performance still possible and practical | Court discretion; may be denied if unreasonable |
| Contract Termination | Article 267 | Material breach with proper notice | Must allow cure period; non-material breaches excluded |
| Direct Damages | Article 272 | Immediate losses from breach | Must be foreseeable and directly caused by breach |
| Loss of Profits | General principles | Future earnings lost due to breach | Must be certain and calculable, not speculative |
| Moral Damages | Civil Code provisions | Harm to reputation or dignity | Limited to cases involving personal or business reputation |
| Interest on Delays | Article 390 | Monetary obligations not timely performed | Standard commercial rates; may be contractually specified |
Comprehensive Remedies Analysis:
UAE law provides comprehensive remedies under Article 272:
Election of Remedies The injured party may choose between demanding specific performance (if still possible) or seeking contract termination with damages.
Damages Categories
- Direct damages resulting immediately from breach
- Loss of profits (if certain and calculable)
- Moral damages for reputation harm
- Interest on delayed monetary obligations
Notice Requirements Proper notice must typically be provided to defaulting parties, allowing reasonable opportunity to cure breaches before termination becomes effective.
Special Contractual Provisions and Protections
Contracts of Adhesion
Article 248 provides special protection for standardized contracts where one party must accept non-negotiable terms. Courts may remove unfair provisions that unduly favor the drafting party.
Force Majeure and Frustration
UAE contract law recognizes force majeure as grounds for excusing contractual performance when extraordinary circumstances beyond parties’ control prevent obligation fulfillment. Recent interpretations have addressed pandemic-related disruptions and their impact on contractual obligations.
Penalty Clauses and Limitations
Article 390 permits predetermined compensation amounts for breach while allowing judicial adjustment to reflect actual damages upon party request.
Dispute Resolution in UAE Contract Law
The UAE legal system emphasizes contractual commitment enforcement while providing fair dispute resolution mechanisms. Parties may choose from several resolution methods:
UAE Courts System Local courts apply both express contractual terms and implied obligations arising from good faith, custom, and legal principles.
Arbitration Mechanisms The UAE supports domestic and international arbitration through specialized centers, particularly in Dubai and Abu Dhabi.
Mediation Services. Alternative dispute resolution methods are increasingly recognized as efficient means of resolving contractual disputes.
Governing Law and Jurisdiction Considerations
Contracts may specify governing law and jurisdiction clauses, though certain restrictions apply. UAE courts generally respect party autonomy in selecting applicable law, provided it doesn’t conflict with UAE public policy or mandatory provisions.
Financial free zones often operate under modified regulatory frameworks that may incorporate elements of common law while maintaining consistency with fundamental UAE legal principles.
Practical Considerations for Contracting in the UAE
Documentation Requirements
While verbal contracts are legally recognized, written documentation provides essential evidence of terms and conditions. Complex commercial agreements should address:
- Detailed performance specifications
- Payment terms and conditions
- Force majeure provisions
- Dispute resolution mechanisms
- Governing law selections
Cultural and Legal Sensitivity
Understanding the intersection of Islamic principles with modern commercial law enhances contractual effectiveness. Parties should consider cultural norms and legal requirements when structuring agreements.
Compliance with Sector-Specific Regulations
Certain contracts require compliance with specialized laws and regulations, particularly in regulated sectors such as banking, insurance, and real estate development.
The comprehensive nature of UAE contract law, rooted in both Islamic jurisprudence and modern civil law principles, provides a robust framework supporting diverse commercial relationships while maintaining flexibility to address the UAE’s evolving business environment. This legal foundation ensures that contractual obligations are honored while providing fair mechanisms for dispute resolution when disagreements arise.



