Launching Your Enterprise in the DMCC Free Zone
The Dubai Multi Commodities Centre occupies a distinctive position within the UAE’s free zone landscape. Unlike sector-specific jurisdictions, the DMCC accommodates a broad spectrum of commercial activities while maintaining particular strength in commodities trading, professional services, and emerging digital sectors. The free zone currently hosts over 25,000 registered companies and contributes approximately 15% of Dubai’s foreign direct investment inflows.
Located in the Jumeirah Lakes Towers district, the DMCC benefits from direct connectivity to Jebel Ali Sea and Air Ports through dedicated logistics infrastructure. This geographic advantage makes it particularly suitable for businesses engaged in international trade, import-export operations, and supply chain management. The free zone’s regulatory framework balances operational flexibility with rigorous compliance standards, reflecting the UAE’s commitment to international financial transparency and anti-money laundering protocols.
Strategic Overview and Economic Significance
The DMCC’s transformation from a niche commodities exchange into a comprehensive global business district positions it as a vital artery for international trade and professional services. The authority has proactively integrated federal mandates such as the UAE Corporate Tax regime and enhanced Anti-Money Laundering protocols into its incorporation workflow, creating a 2026 operational environment defined by a digital-first philosophy where the entirety of the company formation process is conducted through a centralized online portal.
Target Audiences and Investor Profiles
The DMCC attracts three primary investor categories:
- International trading companies requiring a UAE presence for accessing regional markets while maintaining full foreign ownership
- Professional service providers including consultancies, legal firms, and financial advisors seeking a tax-efficient base with minimal capital requirements
- Digital economy ventures in cryptocurrency, artificial intelligence, and gaming that benefit from specialized regulatory frameworks and sector-specific support infrastructure
Typical Use Cases
Companies typically select the DMCC for regional headquarters operations, holding company structures, commodity trading platforms, or as operational bases for serving clients across the Middle East and Africa. The free zone’s reputation for regulatory sophistication makes it particularly attractive for businesses requiring credibility with international banking partners and institutional clients.
What Is Dubai Multi Commodities Centre?
The DMCC operates as an independent regulatory authority established under UAE federal law. It functions as both a free zone administrator and a specialized economic zone with distinct legal and commercial frameworks separate from mainland Dubai regulations.
Governance and Regulatory Structure
The DMCC Authority serves as the primary regulator, overseeing all aspects of company formation, licensing, and ongoing compliance. The authority maintains autonomy in setting operational standards while coordinating with federal bodies including the Federal Tax Authority, the Financial Intelligence Unit, and the Central Bank on matters requiring national-level oversight.
Geographic Location and Infrastructure
Situated at the heart of the Jumeirah Lakes Towers district, the DMCC encompasses a comprehensive business infrastructure supported by a sophisticated logistics corridor that connects the Jebel Ali Sea and Air Ports. This strategic location facilitates seamless transitions for goods between global markets and the domestic economy, making it particularly advantageous for businesses engaged in international trade operations.
Sector Orientation and Specialized Centers
The DMCC organizes its authorizations into several broad families, including trading, services, and industrial sectors. In 2026, the free zone has further stratified its offerings to cater to the burgeoning digital economy through specialized centers:
- DMCC Crypto Centre: The world’s largest concentration of Web3 and blockchain enterprises, categorized into non-regulated Track A (proprietary trading and DLT software development) and regulated Track B (Virtual Asset Service Providers requiring VARA licensing)
- AI Centre: Bespoke packages for artificial intelligence ventures with discounted license fees and specialized office solutions
- Gaming Centre: Dedicated support infrastructure for gaming companies with bundled setup offerings priced at approximately AED 31,000 for the first year
Why Choose Dubai Multi Commodities Centre for Your Business
Selecting the DMCC over alternative jurisdictions involves evaluating several strategic advantages that extend beyond basic tax benefits. Each consideration carries practical implications for operational efficiency, compliance obligations, and long-term business sustainability.
Ownership Rules and Foreign Investor Rights
The DMCC offers 100% foreign ownership across all permitted business activities, eliminating the need for local sponsors or partners. This ownership structure provides complete control over business decisions, profit distribution, and strategic direction. Foreign investors retain full capital repatriation rights, allowing unrestricted transfer of profits, dividends, and capital back to their home countries without withholding taxes or currency controls.
Unlike mainland company structures that historically required 51% UAE national ownership for certain activities, free zone company formation through the DMCC ensures that international investors maintain absolute control while accessing regional markets.
Tax Treatment and Exemptions Under UAE Regulations
DMCC companies benefit from a favorable tax environment within the UAE’s regulatory framework. The free zone operates under a zero percent corporate income tax regime for qualifying activities, though businesses must navigate the federal Corporate Tax requirements introduced in 2023. Companies may qualify as a Qualifying Free Zone Person (QFZP) and maintain a 0% tax rate on qualifying income, provided they demonstrate adequate economic substance through physical office presence and qualified staff.
Value Added Tax (VAT) at the standard 5% rate applies to taxable supplies, but free zone status provides certain exemptions and benefits for international transactions. Import duties are waived for goods entering the free zone, though duties apply when goods move from the free zone into the UAE mainland market.
Industry Specialization and Permitted Activities
The DMCC supports over 2,100 distinct business activities aligned with Dubai Department of Economy and Tourism classifications. A single DMCC license can accommodate up to six related business activities within the same two-digit activity group, providing operational flexibility for businesses with diverse service offerings.
The complexity lies in the licensing structure where activities from different divisions or unrelated sectors trigger additional annual fees or require multiple licenses. This framework encourages strategic planning during the initial setup phase to optimize licensing costs and operational scope.
Administrative Efficiency and Digital Processes
The 2026 operational environment prioritizes digital transformation, where the entire company formation process from name reservation to electronic license issuance occurs through a centralized online portal. This paradigm shift significantly reduces administrative friction, allowing most standard businesses to achieve registration within ten working days.
The digital-first approach extends to ongoing compliance, visa processing, and license renewals, minimizing physical documentation requirements and in-person visits to government offices. Electronic signature capabilities and video verification protocols further streamline processes that traditionally required physical presence.
Infrastructure, Facilities, and Business Ecosystem
The DMCC provides comprehensive business infrastructure spanning flexible workspace solutions, dedicated office buildings, and industrial warehousing facilities. The free zone’s ecosystem includes banking partnerships, legal service providers, and professional consultancies, creating a self-contained business environment.
Networking opportunities through the DMCC member community, industry-specific events, and trade missions facilitate business development and partnership opportunities. The authority’s reputation and established relationships with international regulatory bodies enhance credibility when engaging with global clients and financial institutions.
Types of Companies You Can Register in Dubai Multi Commodities Centre
The determination of legal structure represents a critical decision that dictates liability profiles, ownership flexibility, and compliance obligations. The DMCC provides three primary structures for new entrants, each serving distinct business requirements.
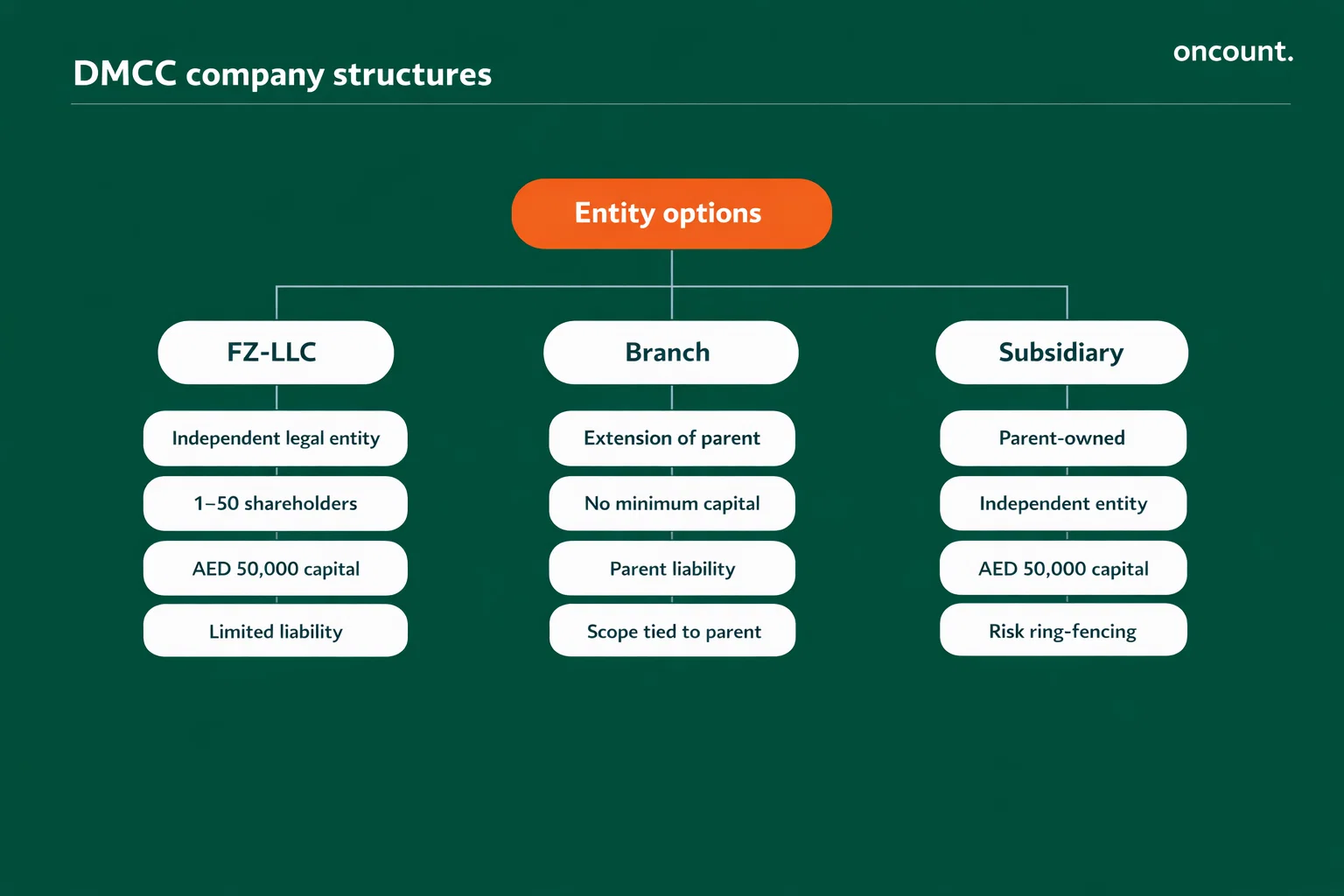
Free Zone Limited Liability Company (FZ-LLC)
The FZ-LLC structure operates as an independent legal entity with its own legal personality, providing clear separation between the company’s liabilities and the personal assets of shareholders. This structure accommodates single-shareholder configurations or multi-shareholder arrangements with up to 50 participants, who may be individuals or corporate bodies.
The minimum share capital requirement stands at AED 50,000, providing a flexible entry point for most startups and professional firms. Shareholders bear liability limited to their capital contributions, protecting personal assets from business obligations beyond their investment. This structure proves particularly suitable for businesses seeking operational independence, planning to raise external funding, or requiring separate legal personality for contractual relationships.
Branch of a Local or Foreign Company
A branch operates as a legal extension of its parent company rather than a separate legal entity. The parent company retains full financial and legal responsibility for all activities conducted through the DMCC branch, eliminating the requirement for minimum share capital deposits.
This structure proves advantageous for established corporations seeking a UAE presence without creating a separate subsidiary. The branch can conduct business activities consistent with the parent company’s operations, though it cannot engage in activities beyond the parent’s scope. Financial reporting consolidates with the parent company, simplifying accounting while requiring that audited financials reflect the entire corporate group.
Subsidiary Structure
A wholly-owned subsidiary functions as a separate limited liability company while maintaining 100% ownership by a parent company. This structure enables clear ring-fencing of liabilities while maintaining full corporate control, making it suitable for risk management strategies where the parent company seeks to isolate specific business lines or market exposures.
The subsidiary maintains independent legal personality, requiring separate financial statements, bank accounts, and regulatory filings. This structure provides operational autonomy while ensuring that strategic control remains with the parent company through share ownership.
| Feature | FZ-LLC | Branch | Subsidiary |
| Legal Status | Independent Entity | Extension of Parent | Independent Entity |
| Minimum Capital | AED 50,000 | None | AED 50,000 |
| Shareholder Limit | 1-50 | 1 (Parent) | 1 (Parent) |
| Liability | Limited to Capital | Full Parent Liability | Limited to Capital |
| Annual Audit | Mandatory | Mandatory | Mandatory |
Types of Business Licenses in Dubai Multi Commodities Centre
License selection directly impacts operational scope, banking relationships, visa entitlements, and compliance requirements. The DMCC categorizes licenses across trading, services, and industrial classifications, with specialized variants for digital economy sectors.

Trading License
Trading licenses authorize import, export, distribution, and general trading activities for commodities and goods. License holders can engage in wholesale and retail operations, though retail activities targeting UAE mainland consumers may require additional approvals. Trading licenses prove essential for businesses engaged in commodity trading, import-export operations, or distribution networks.
The license supports inventory management, warehousing operations, and logistics coordination. Banking institutions typically require trading licenses for trade finance facilities, letters of credit, and inventory financing arrangements.
Service License
Service licenses cover professional services, consultancy, technology services, and business support activities. This category encompasses management consultancy, legal services, financial advisory, marketing agencies, and IT services. Service license holders conduct client-facing professional work without handling physical goods or inventory.
This license type supports knowledge-based businesses requiring minimal physical infrastructure. Visa quotas for service licenses typically align with office space rather than business volume, making flexi-desk and serviced office solutions viable for smaller professional practices.
Industrial License
Industrial licenses authorize manufacturing, processing, and production activities within designated industrial zones. License holders can operate production facilities, conduct assembly operations, and manage quality control processes. This license category requires warehouse or industrial space rather than standard office facilities.
Industrial operations face additional regulatory oversight regarding environmental compliance, safety standards, and waste management. The license supports businesses seeking to establish manufacturing presence serving regional markets while benefiting from free zone import duty exemptions on raw materials and equipment.
Specialized Digital Economy Licenses
The 2026 framework includes tailored license packages for crypto, AI, and gaming sectors. These specialized licenses bundle regulatory approvals, office solutions, and sector-specific support services. Crypto licenses distinguish between Track A (non-regulated proprietary trading and DLT development) and Track B (regulated Virtual Asset Service Providers requiring VARA licensing alongside DMCC incorporation). AI and Gaming packages offer first-year bundled pricing at approximately AED 31,000, inclusive of basic licensing and co-working access.
Step-by-Step Process to Set Up a Business in Dubai Multi Commodities Centre
The incorporation process follows a structured seven-step sequence, moving from initial planning through final licensing and banking integration. Understanding not only the procedural steps but also the strategic implications and common challenges ensures efficient navigation of the setup journey.
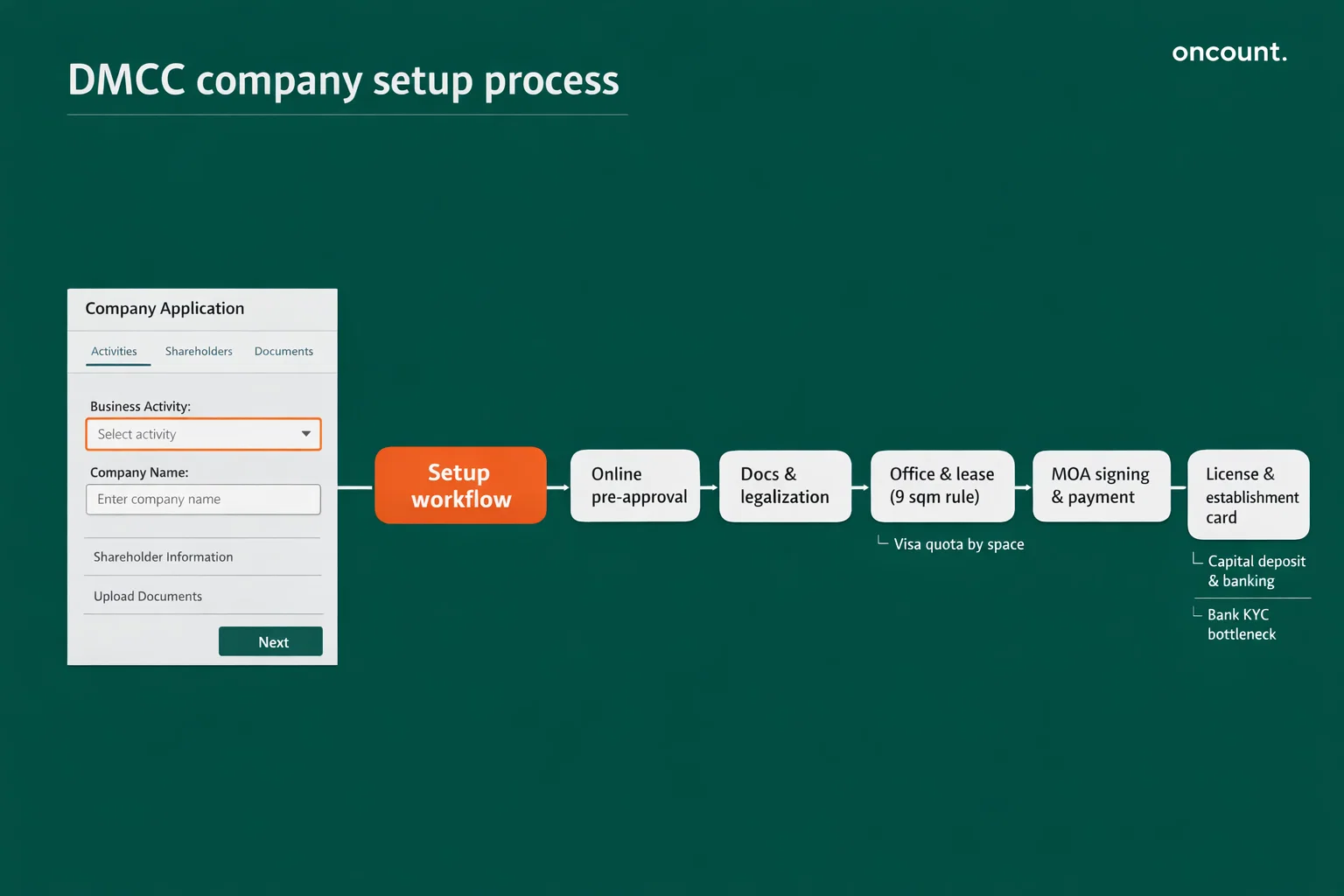
Step 1: Activity Selection and Name Reservation
The process initiates with selecting business activities from the comprehensive list of over 2,100 options aligned with Dubai Department of Economy and Tourism classifications. Strategic activity selection proves critical because a single DMCC license accommodates up to six related activities within the same two-digit activity group, while unrelated activities trigger additional fees or multiple license requirements.
Simultaneously, applicants must select a trade name complying with UAE naming conventions. Prohibited terms include references to political groups, religious affiliations, or offensive language. If a business name incorporates a person’s name, that individual must be a partner or shareholder. Name reservation carries a non-refundable fee of AED 1,000 and remains valid for 60 days once approved. The selected activities are cross-referenced against the proposed name to ensure consistency and regulatory compliance.
Step 2: Online Pre-Approval and Initial Due Diligence
Submission of the pre-approval application via the DMCC portal initiates the authority’s due diligence process. The review team examines applications against multiple criteria including background screenings of shareholders and directors, compliance verification of proposed activities, and document authentication. For standard activities, Initial Approval typically processes within two to five business days.
Complex or regulated activities require Third-Party No Objection Certificates from external regulators, significantly extending approval timelines:
| Activity Sector | External Regulator | Typical Approval Time |
| Healthcare / Pharmacy | Dubai Health Authority | 2-4 Weeks |
| Financial Services | Central Bank / SCA | 8-12 Weeks |
| Education / Training | KHDA | 4-8 Weeks |
| Telecommunications | TDRA | 2-4 Weeks |
| Crypto (Regulated) | VARA | 5-12+ Weeks |
| Food & Beverages | Dubai Municipality | 2-3 Weeks |
Step 3: Document Preparation and Legalization
This phase often proves most time-intensive for international investors. Documents issued outside the UAE require multi-stage attestation involving notarization in the home country, attestation by the local Ministry of Foreign Affairs, and legalization by the UAE Embassy or Consulate.
For individual shareholders, required documentation includes color passport copies, proof of residential address through utility bills or bank statements not older than three months, and bank reference letters. Corporate shareholders must provide attested Certificates of Incorporation, Memoranda of Association, and Board Resolutions authorizing the new setup. Document preparation timelines vary significantly based on home country processes, often requiring four to eight weeks for complete attestation chains.
Step 4: Physical Space Selection and Lease Finalization
A registered office address constitutes a mandatory requirement for license issuance. The DMCC offers workspace solutions ranging from flexi-desks for solo entrepreneurs to dedicated warehouses for industrial operations. Office selection directly determines visa quota entitlements based on the 9-square-meter rule requiring 9 square meters of office space per sponsored employee visa.
| Office Type | Description | Annual Cost (AED) | Visa Quota |
| Flexi Desk | Shared workstation in co-working lounge | 15,000-20,000 | Up to 3 visas |
| Serviced Desk | Dedicated desk with shared amenities | 24,000-35,000 | 4-5 visas |
| Private Office | Dedicated fitted office space | 50,000+ | 1 visa per 9 sqm |
| Warehouse | Industrial units for manufacturing | 80,000+ | Higher based on size |
The 9-square-meter regulation ensures businesses maintain genuine operational presence and prevents shell company proliferation. Companies planning significant hiring must secure adequate space during initial setup to avoid visa quota constraints limiting business growth.
Step 5: Registration, Payment, and MOA Signing
Following office lease finalization, the DMCC portal generates the Memorandum and Articles of Association based on approved activities and structure. In 2026, most MOAs utilize electronic signature protocols, though certain cases require video call verification where original passports are sighted by DMCC executives.
After MOA signing, applicants settle registration and licensing fees. Standard annual license fees start at AED 20,285, with additional costs for establishment cards and visa quotas. Payment processing typically completes within one business day, advancing the application to final licensing stages.
Step 6: Licensing and Establishment Card Issuance
Upon successful processing of payments and documents, the DMCC issues the Certificate of Registration, Share Certificates, and E-license. Simultaneously, the company receives its Establishment Card, also known as the Company Immigration Card. This card serves as the foundational document connecting the company to the UAE immigration system, enabling sponsorship of residency visas for owners, partners, and employees. Without the Establishment Card, no visa-related processes can proceed.
Step 7: Capital Deposit and Banking Integration
The final formal setup step involves depositing minimum share capital. For LLCs with AED 50,000 share capital, the DMCC provides a streamlined Portal Deposit mechanism where funds are credited to the company’s portal account for use in paying DMCC services like visas or renewals. Companies with higher share capital requirements must deposit funds into a UAE corporate bank account and submit bank confirmation letters to the DMCC within 180 days of license issuance.
Banking integration represents a critical bottleneck where corporate account opening can add two to four weeks to timelines despite rapid license processing. Digital banks like Wio Bank, Mashreq Neo Biz, and Zand offer online account opening within 72 to 120 hours, while traditional banks like Emirates NBD or ADCB apply more rigorous Know Your Customer scrutiny requiring detailed business plans and source of wealth documentation.
Documents Required for Company Registration
Document requirements vary based on shareholder type and corporate structure, though all applications share certain foundational documentation. Understanding attestation requirements and processing timelines proves essential for avoiding delays during the incorporation process.
Personal Documents for Individual Shareholders
Individual shareholders must provide color passport copies with minimum six-month validity. Proof of residential address through utility bills, bank statements, or government correspondence dated within the preceding three months verifies current residence. Bank reference letters from the shareholder’s primary banking institution confirm account standing and financial credibility.
For shareholders resident in countries requiring document attestation, passport copies must undergo notarization by licensed notaries, followed by Ministry of Foreign Affairs attestation in the home country, and final legalization by the UAE Embassy or Consulate. This multi-stage process often requires four to eight weeks depending on home country procedures and embassy processing times.
Corporate Shareholder Documents
Corporate entities serving as shareholders must provide attested Certificates of Incorporation demonstrating legal establishment in their home jurisdiction. The Memorandum and Articles of Association or equivalent constitutional documents outline corporate purposes, share structures, and governance frameworks. Board Resolutions specifically authorizing the DMCC company formation and designating authorized signatories prove that the parent company has properly approved the investment.
For publicly traded companies, additional documentation including recent annual reports, financial statements, and shareholder registers may be required. All corporate documents require the same attestation chain as individual documents, beginning with notarization and progressing through Ministry of Foreign Affairs attestation and UAE Embassy legalization.
Additional Supporting Materials
Specific business activities may require additional documentation. Healthcare activities necessitate professional qualification certificates for medical practitioners. Educational services require academic credentials and teaching certifications. Financial services demand regulatory licenses from home country financial authorities.
Business plans outlining operations, target markets, and financial projections support applications for certain regulated activities or when seeking specialized office solutions. Source of funds declarations and bank statements covering six-month periods demonstrate financial capacity, particularly for investor visa applications under the 2026 economic substance requirements.
Cost of Setting Up a Business in Dubai Multi Commodities Centre
Understanding the complete cost structure enables accurate budgeting and prevents unexpected expenses during the incorporation process. Costs span license fees, office solutions, visa allocations, and ongoing compliance obligations.
License Fees and Registration Charges
Standard annual license fees begin at AED 20,285 for basic business activities. This base fee covers the primary license issuance and first-year regulatory oversight. Companies selecting multiple unrelated business activities face additional charges, with each supplementary license potentially adding AED 10,000 to AED 15,000 annually depending on activity classification.
Name reservation carries a non-refundable fee of AED 1,000, payable upon application submission. Registration fees covering MOA preparation, share certificate issuance, and administrative processing typically total AED 3,000 to AED 5,000. Certificate attestation and document processing may incur additional charges of AED 2,000 to AED 3,000 depending on document volume and complexity.
Office Space and Workspace Packages
Office costs represent significant ongoing expenses varying by workspace type and location. Flexi-desk solutions in co-working environments range from AED 15,000 to AED 20,000 annually, supporting up to three visa allocations. Serviced desk arrangements with dedicated workstations cost AED 24,000 to AED 35,000 annually, accommodating four to five visas.
Private offices begin at AED 50,000 annually for small fitted spaces, scaling upward based on square footage and location within the DMCC district. Industrial warehouse facilities for manufacturing operations start at AED 80,000 annually, with pricing determined by space requirements and specialized infrastructure needs.
Visa Costs and Immigration Fees
Each residency visa entails multiple cost components spanning entry permits, medical examinations, Emirates ID processing, and visa stamping. Entry permit fees approximate AED 3,000 per visa. Medical fitness testing at government-approved centers costs AED 300 to AED 500 per person. Emirates ID application and processing totals AED 370, covering the biometric card valid for visa duration.
Visa stamping or digital visa issuance fees amount to AED 3,000 to AED 5,000 per visa depending on validity period. Two-year residency visas, now standard for most DMCC companies, carry higher initial costs but prove more economical than annual renewals. Health insurance activation, mandatory for all residents, costs AED 600 to AED 2,500 annually per person based on coverage level and age.
Factors Influencing Total Pricing
Total setup costs range from AED 45,000 for minimal single-shareholder service companies with flexi-desk solutions to AED 150,000 or more for multi-shareholder trading companies requiring private offices and multiple visa allocations. Activity type significantly impacts pricing, with regulated activities requiring third-party approvals adding AED 10,000 to AED 30,000 in additional regulatory fees and extended professional service engagement.
The 2026 specialized packages for crypto, AI, and gaming companies offer bundled first-year pricing at approximately AED 31,000, including basic licensing and co-working access. These packages prove cost-effective for technology startups prioritizing rapid market entry over extensive physical infrastructure.
Free Zone vs Mainland Company Setup
Choosing between free zone and mainland company structures involves evaluating ownership flexibility, market access, tax treatment, physical presence requirements, and regulatory oversight. Each option serves distinct strategic objectives requiring careful assessment against business goals.
Ownership and Control Structures
Free zone companies permit 100% foreign ownership across all business activities without requiring UAE national sponsors or partners. Mainland companies historically mandated 51% UAE national ownership for certain commercial activities, though recent regulatory reforms now allow 100% foreign ownership for most mainland activities subject to Ministry of Economy approvals.
Despite ownership liberalization, mainland structures may still face sector-specific restrictions or require local service agents for certain activities. Free zone structures guarantee unconditional foreign ownership, providing certainty for international investors concerned about control and profit distribution.
Market Access and Operational Scope
Mainland companies can directly serve UAE consumers and businesses without restrictions, operating anywhere within the UAE and trading freely within the domestic market. Free zone companies face limitations on direct mainland transactions, typically requiring mainland distributors or agents for substantial domestic business.
However, free zone companies excel in international operations, import-export activities, and regional headquarters functions. For businesses primarily serving international markets or requiring UAE presence for banking and logistics infrastructure rather than domestic market access, free zone structures often prove more efficient.
Taxation and Financial Considerations
Both free zone and mainland companies now fall under UAE Corporate Tax regulations introduced in 2023. Free zone companies may qualify as Qualifying Free Zone Persons maintaining 0% tax rates on qualifying income, provided they meet substance requirements and refrain from conducting business with mainland UAE.
Mainland companies subject to Corporate Tax face 9% rates on taxable income exceeding AED 375,000. Both structures must register for VAT if exceeding the mandatory threshold of AED 375,000 in annual taxable supplies, though voluntary registration is available for businesses below this threshold anticipating future growth.
Office Requirements and Physical Presence
Free zone companies must maintain registered offices within their specific free zone, with visa quotas tied directly to office space under the 9-square-meter rule. Mainland companies require physical office space meeting Ejari registration requirements, though regulations permit flexible arrangements including business centers and shared office solutions.
Free zone office costs often exceed mainland alternatives for equivalent space, though free zones provide integrated infrastructure and business services justifying premium pricing. Mainland operations may require separate arrangements for business support services readily available within free zone ecosystems.
Regulatory Oversight and Compliance Framework
Free zone companies answer primarily to their specific free zone authority with streamlined regulatory processes and digital-first platforms. Mainland companies engage with Department of Economic Development authorities across Dubai’s various districts, potentially facing more complex multi-agency coordination.
Compliance requirements converge between structures regarding federal obligations including Corporate Tax, VAT, AML/CFT protocols, and Ultimate Beneficial Ownership reporting. Free zones often provide enhanced support infrastructure and guidance through dedicated business development teams familiar with international investor needs.
Accounting, Tax, and Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Operating a DMCC company requires ongoing compliance with multiple regulatory frameworks spanning federal UAE obligations and free zone-specific requirements. The 2026 governance environment emphasizes continuous compliance rather than periodic tick-box exercises.
Corporate Tax Registration and Filing
All entities incorporated after March 1, 2024 must register for Corporate Tax and obtain a Tax Registration Number within 90 days of incorporation. Failure to meet this deadline triggers automatic penalties of AED 10,000. Companies must file annual tax returns and remit any due tax within nine months of their financial year end.
DMCC companies may qualify as Qualifying Free Zone Persons eligible for 0% tax rates on qualifying income, provided they maintain adequate economic substance through physical office presence and qualified staff, and avoid conducting business with mainland UAE. Non-qualifying income faces standard 9% Corporate Tax rates on profits exceeding AED 375,000.
| Tax Obligation | Deadline | Penalty for Default |
| CT Registration | 90 days from incorporation | AED 10,000 |
| Annual Return Filing | 9 months from year-end | AED 500-1,000 per month |
| Record Keeping | 7 years maintenance | Variable administrative fines |
| Record Updates | 20 business days from change | AED 1,000-10,000 |
VAT Registration and Compliance
Companies must register for VAT if annual taxable supplies exceed AED 375,000, the mandatory registration threshold. Voluntary registration is available for businesses with taxable supplies between AED 187,500 and AED 375,000, beneficial for claiming input VAT on business expenses. VAT returns require quarterly filing for most businesses, with specific requirements for maintaining tax invoices, accounting records, and supporting documentation.
Free zone companies enjoy certain VAT advantages for international transactions, with designated zones qualifying for zero-rated supplies on goods and services exported outside the UAE. However, supplies from free zones to mainland UAE typically attract standard 5% VAT rates.
Economic Substance Regulations
Economic Substance Regulations require companies conducting relevant activities to demonstrate genuine economic presence in the UAE through adequate physical offices, qualified employees, and core income-generating activities performed locally. Relevant activities include banking, insurance, investment fund management, lease-finance, headquarters operations, shipping, holding company activities, intellectual property, and distribution and service center operations.
Annual Economic Substance Reports must be filed with the Ministry of Finance within 12 months of the financial year end. Companies failing substance tests face penalties ranging from AED 50,000 for first violations to AED 300,000 for continued non-compliance, with potential license revocation for persistent failures.
Anti-Money Laundering and Counter-Terrorism Financing
The UAE AML/CFT framework requires all DMCC businesses to register on the goAML portal regardless of business type. Companies must establish internal AML policies, appoint designated compliance officers, and conduct regular staff training. The 2026 framework introduces standalone proliferation financing offenses, mandating companies screen all partners and transactions against global watchlists preventing illicit trade in materials for weapons of mass destruction.
Risk-based customer due diligence must be performed on all clients, with enhanced scrutiny for high-risk relationships involving politically exposed persons, high-value transactions, or jurisdictions identified on international watch lists. Transaction monitoring systems should flag suspicious activities for potential reporting to the Financial Intelligence Unit.
Ultimate Beneficial Ownership Reporting
All DMCC companies must maintain UBO Registers at registered offices and submit details of individuals owning or controlling 25% or more of the company to the DMCC Authority. If no individual meets the threshold, the UBO is defined as the person holding the highest management position such as CEO or Managing Director.
Any modification to UBO data must be updated on the portal within 15 days, with non-compliance attracting administrative penalties up to AED 100,000. Accurate UBO reporting proves essential for banking relationships, as financial institutions conduct their own beneficial ownership verification as part of Know Your Customer processes.
Annual Audit Requirements and Financial Reporting
Every DMCC-registered company excluding certain branch office configurations must submit audited financial statements annually. Audits must be performed by DMCC-approved auditors listed on the Approved Auditors List. The audit report serves as a prerequisite for license renewal and verifies financial health and regulatory compliance.
Financial statements should comply with International Financial Reporting Standards, maintaining books and records for minimum seven-year periods. The Federal Tax Authority may request historical financial information during tax audits or compliance reviews, making meticulous record-keeping essential for avoiding penalties and disputes.
Common Mistakes When Setting Up a Free Zone Company
Understanding frequent errors made during DMCC company formation enables proactive risk mitigation and smoother incorporation processes. These mistakes often extend timelines, increase costs, or create compliance vulnerabilities requiring remediation.
Licensing and Activity Selection Errors
Many investors underestimate the importance of precise activity selection, choosing generic activities that later prove insufficient for specific business operations. Banking institutions and clients may question whether contracted services fall within licensed activities, potentially delaying transactions or requiring license amendments. Companies should invest time identifying all relevant activities during initial setup, recognizing that adding activities later triggers amendment fees and administrative delays.
Selecting activities from multiple unrelated groups without understanding the cost implications leads to unexpected fees. A single license accommodating six activities within the same two-digit group proves far more economical than multiple licenses or supplementary activity charges. Strategic activity clustering during planning prevents unnecessary expenses.
Banking Relationship Challenges
Failing to prepare comprehensive documentation packages before approaching banks represents a common error extending account opening timelines. Banks require detailed business plans, shareholder source of wealth documentation, and clarity on transaction types and volumes. Companies submitting incomplete applications face repeated information requests and extended processing periods.
Many entrepreneurs underestimate the enhanced scrutiny applied by UAE banks following international compliance standards. Crypto businesses, money service firms, and high-risk sectors should engage banks early, potentially during pre-approval stages, to confirm account opening feasibility before committing to full company formation. Pre-banking discussions prevent situations where companies obtain licenses but cannot secure essential banking facilities.
Tax Registration Timing Failures
The 90-day Corporate Tax registration window represents a hard deadline triggering automatic AED 10,000 penalties for late compliance. Many new companies focus on operational launch while neglecting immediate tax registration obligations. Incorporating tax registration into standard setup checklists prevents costly oversights.
Companies also frequently misunderstand Qualifying Free Zone Person criteria, assuming automatic 0% tax rates without demonstrating required economic substance. Failing to maintain adequate office space, qualified staff, or proper documentation to prove substance results in unexpected tax liabilities when authorities review QFZP status during audits or filing reviews.
Compliance Planning Deficiencies
Many startups treat compliance as a post-launch concern rather than integrating requirements into foundational systems and processes. Establishing AML policies, appointing compliance officers, and implementing UBO tracking systems proves far easier during setup than retrofitting these frameworks into established operations.
Companies often neglect the 15-day UBO update requirement, discovering compliance gaps only when facing penalties or banking relationship issues. Building systematic processes for monitoring ownership changes and promptly updating registers prevents administrative penalties and maintains regulatory good standing.
Inadequate record-keeping systems create challenges during annual audits and tax filing periods. Establishing proper accounting infrastructure, maintaining contemporaneous transaction documentation, and organizing records according to audit requirements from day one prevents scrambling during compliance deadlines.
Why Work With a Professional Business Setup and Accounting Firm
Engaging experienced business setup consultants and accounting professionals delivers measurable value through risk mitigation, efficiency gains, and compliance optimization. The decision involves evaluating cost against the operational advantages and long-term sustainability benefits professional guidance provides.
Jurisdiction Selection and Strategic Planning
Professional advisors provide objective analysis comparing DMCC against alternative free zones and mainland structures based on specific business requirements. This includes evaluating industry focus, client market location, visa needs, and long-term growth plans. Advisors familiar with multiple jurisdictions identify optimal structures that clients unfamiliar with UAE options might overlook.
Strategic planning extends to activity selection, ensuring comprehensive coverage while minimizing licensing costs through intelligent activity clustering. Advisors anticipate future business development needs, recommending initial structures accommodating expansion without requiring costly restructuring later.
Documentation Management and Process Coordination
Document attestation chains, particularly for international investors, involve complex multi-country processes with varying requirements and timelines. Professional firms manage these processes, coordinating with notaries, foreign ministries, and UAE embassies to ensure proper documentation flow. This expertise prevents common errors including improper attestation sequences, expired documents, or missing certifications causing application rejections.
Firms maintain current knowledge of changing documentation requirements, digital verification protocols, and acceptable substitutions when standard documents prove unavailable. They also coordinate timing across multiple parallel processes, ensuring documents arrive when needed rather than expiring before use.
Regulatory Compliance and Ongoing Support
Professional accounting firms provide compliance frameworks encompassing Corporate Tax registration, VAT filing, Economic Substance reporting, and AML policy development. This integrated approach ensures companies meet all obligations rather than addressing requirements piecemeal as penalties arise.
Ongoing accounting support maintains proper books and records in formats satisfying both audit requirements and tax filing needs. Professional firms familiar with DMCC-approved auditor expectations structure financial records appropriately from inception, preventing expensive remediation when annual audits commence.
Tax advisors optimize structures for legitimate tax efficiency, ensuring companies properly claim QFZP status where applicable while avoiding aggressive positions triggering authority scrutiny. They also navigate the intersection of free zone benefits with federal tax obligations, an increasingly complex area as UAE tax frameworks mature.
Cost Optimization and Value Engineering
Experienced consultants identify cost-saving opportunities through package selection, visa allocation strategies, and office solution choices aligned with actual business needs rather than maximum options. They prevent over-specification during initial setup when businesses operate with limited resources, while ensuring structures accommodate anticipated growth.
Understanding which costs prove essential versus discretionary enables informed decisions. Professional guidance helps companies allocate budgets to compliance and infrastructure delivering long-term value while avoiding unnecessary expenses on features providing marginal benefit.
The investment in professional services typically recovers through avoided penalties, faster processing, and optimal structure selection. For international investors unfamiliar with UAE systems, professional guidance often proves essential for successful incorporation and sustainable operations.