Establishing Your Enterprise in Dubai Airport Free Zone
Dubai Airport Free Zone has positioned itself as a premier destination for international business since 1996. Now part of Dubai Integrated Economic Zones (DIEZ), the authority hosts over 2,000 companies from more than 100 countries.
The zone’s appeal lies in its proximity to Dubai International Airport (DXB), enabling access to 150+ airlines and 220+ global destinations. This location advantage translates into rapid cargo clearance and 24/7 customs operations—critical factors for businesses requiring precise logistics.
Strategic Positioning in the UAE Economy
DAFZA serves as a cornerstone of the UAE’s economic diversification strategy. The zone minimizes operational friction while maximizing international connectivity, making it ideal for high-value, low-volume trading entities.
The regulatory environment emphasizes transparency and speed, with a highly digitalized approach to company formation. This modernization reflects the UAE’s commitment to remaining competitive in the global business landscape.
Target Business Profiles
DAFZA attracts diverse industries spanning:
- Aviation and aerospace companies
- Luxury goods distributors
- Pharmaceutical manufacturers
- Technology and IT service providers
- Trading and logistics enterprises
- Professional service firms
The zone is particularly suited for businesses requiring immediate airport access, companies seeking 100% foreign ownership, and enterprises targeting regional expansion from a tax-efficient base.
Understanding Dubai Airport Free Zone Authority
DAFZA was established in 1996 under Dubai Law No. 25 of 2009, which grants the authority regulatory autonomy to create and implement licensing and registration rules.
The Implementing Regulations of 2021 modernized the framework, introducing international best practices for corporate governance. These include maintaining an Ultimate Beneficial Owner (UBO) register and enabling virtual general assemblies.
Geographic and Administrative Framework
Located adjacent to Dubai International Airport, DAFZA provides immediate access to one of the world’s busiest aviation hubs. The zone operates independently under its own regulatory framework while aligning with UAE federal laws.
The authority manages all aspects of business licensing, immigration services, and facility allocation through centralized service centers. This one-stop-shop model simplifies administrative procedures for investors.
Industry Focus and Economic Activities
DAFZA offers over 2,000 economic activities across 18 major sectors, aligned with ISIC Rev 4 classification standards. The zone supports trading, services, and light industrial operations.
Specialized infrastructure includes warehousing facilities, cold storage for pharmaceuticals and perishables, and light industrial units for assembly and packaging operations.
Key Advantages of Choosing Dubai Airport Free Zone
Selecting DAFZA over alternative jurisdictions offers distinct operational and financial benefits. Understanding these advantages helps investors align their business strategy with the zone’s unique offerings.
Complete Foreign Ownership Rights
DAFZA permits 100% foreign ownership without requiring a local sponsor or partner. This structure provides full control over business operations, strategic decisions, and profit distribution.
Investors enjoy unrestricted repatriation of capital and profits, with no limitations on currency conversion or fund transfers. This financial flexibility is critical for international businesses managing multi-jurisdictional operations.
Tax Incentives and Exemptions
DAFZA entities benefit from comprehensive tax advantages:
- Zero corporate income tax on qualifying income
- No personal income tax for employees
- 100% exemption from import and export duties (for goods remaining in or exiting the zone)
- VAT exemption for designated free zone transactions
However, businesses must meet “Qualifying Free Zone Person” criteria to maintain 0% corporate tax status. The UAE introduced a federal corporate tax of 9% on profits exceeding AED 375,000 in 2026, though qualifying free zone entities can remain exempt.
Specialized Industry Support
The zone provides sector-specific infrastructure and licensing options. Aviation companies benefit from proximity to DXB, while logistics firms leverage bonded warehousing to defer customs duties.
DAFZA has introduced modern licenses including the Dual License (enabling mainland operations), E-commerce License, and Family Office licenses for wealth management operations.
Digital Efficiency and Processing Speed
The authority’s digitalized approach accelerates business formation. The online portal provides access to over 250 services, including license amendments, visa processing, and facility management.
Most standard licenses are issued within five to six working days following initial approvals, significantly faster than many regional alternatives.
Infrastructure and Business Ecosystem
DAFZA offers plug-and-play office solutions with integrated ICT infrastructure, high-speed connectivity through Etisalat and Du, and in-house facility management.
The DAFZ Industrial Park in Al Qusais, located just 5 km from airport runways, features 33 warehouses with heights up to 11.1 meters, 10 cold-storage facilities, and power availability up to 200kW per unit.
Legal Structures Available for Registration
DAFZA permits several corporate structures, each with distinct ownership, liability, and capital requirements. Selecting the appropriate entity type impacts taxation, banking relationships, and operational flexibility.
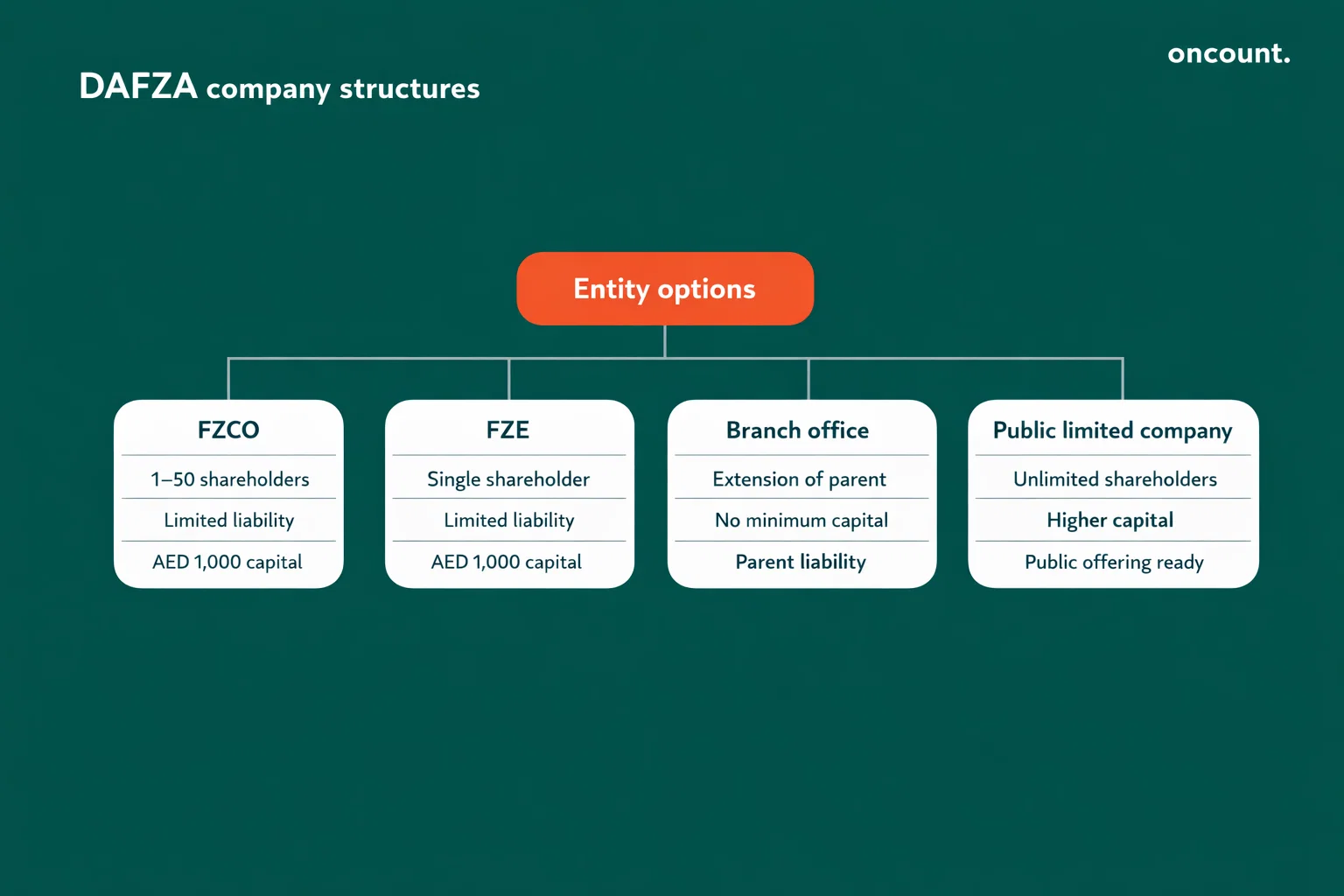
Free Zone Company (FZCO)
The FZCO structure accommodates 1 to 50 shareholders and requires minimum share capital of AED 1,000. This model resembles a Limited Liability Company (LLC), where shareholders can be individuals or corporations.
Liability is limited to the share capital value, protecting personal assets. The FZCO is the most common choice for multi-shareholder ventures and provides a distinct legal presence separate from shareholders.
Free Zone Establishment (FZE)
The FZE structure is designed for single-shareholder entities with minimum share capital of AED 1,000. This option suits sole proprietors or parent companies establishing subsidiaries.
The structure offers the same limited liability protection as an FZCO while simplifying governance requirements due to single ownership. It’s ideal for individual entrepreneurs or wholly-owned corporate subsidiaries.
Branch Office Structure
A branch office serves as an extension of an existing UAE or foreign parent company. No minimum capital requirement applies, as the branch relies on the parent entity’s financial standing.
The parent company remains fully liable for the branch’s obligations. All corporate documents must be notarized and attested by the UAE Embassy in the country of origin, including the Certificate of Incorporation and Board Resolution authorizing the branch establishment.
Public Limited Company (PLC)
The PLC structure accommodates unlimited shareholders with higher minimum capital requirements. This option is designed for large-scale operations and companies planning to list on stock exchanges.
The structure provides greater flexibility for raising capital through public offerings while maintaining compliance with enhanced governance and disclosure requirements.
Available License Categories in DAFZA
License selection determines operational scope, regulatory approvals required, and visa allocations. DAFZA has restructured fees to enhance competitiveness, with standard licenses costing approximately AED 15,000 annually.
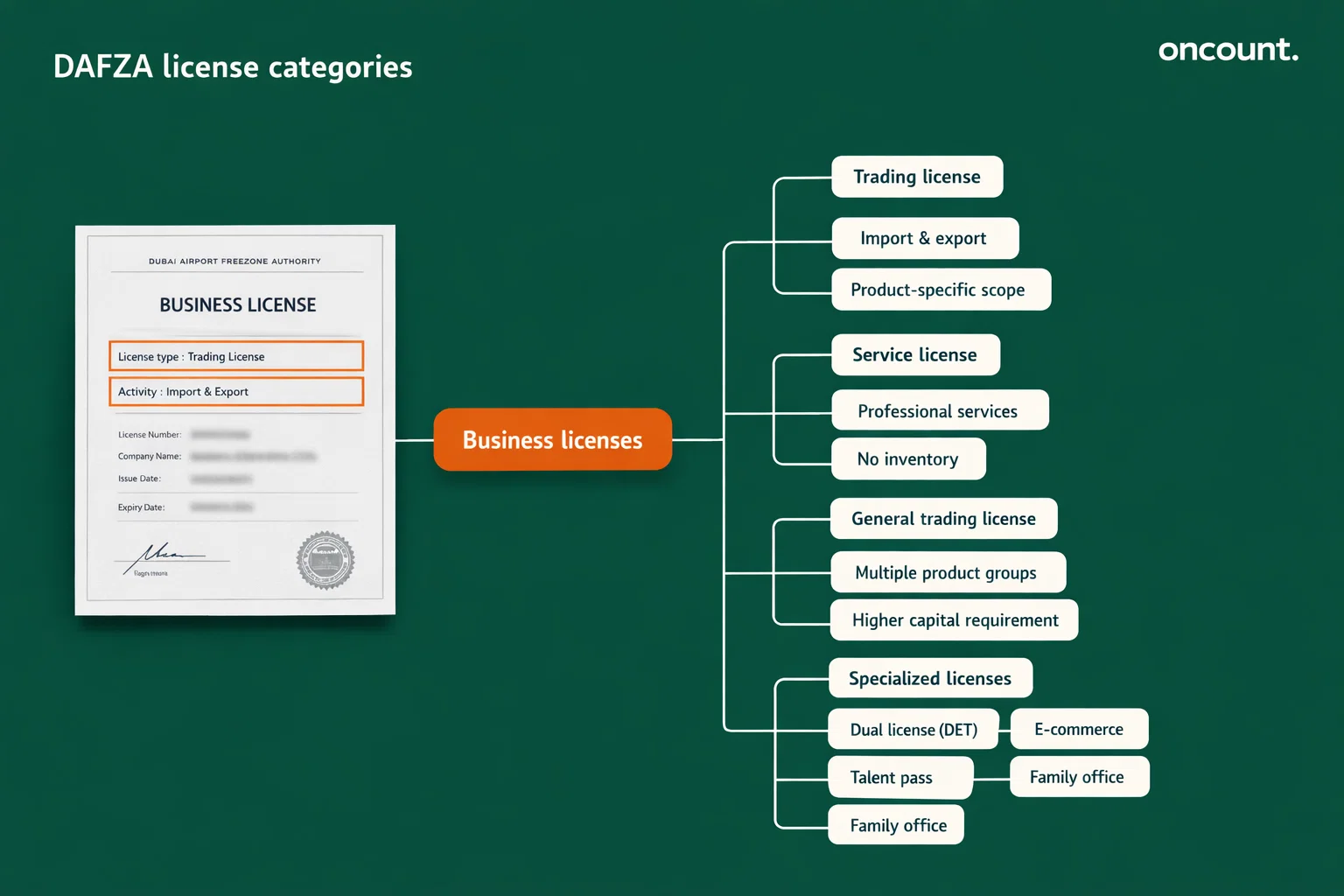
Trading License
The trading license authorizes import, export, re-export, distribution, and storage of specific products listed on the license. This permit is essential for commercial trading operations.
Businesses dealing in regulated products must obtain additional approvals from relevant UAE ministries such as the Ministry of Health or Dubai Health Authority. The license scope is limited to activities explicitly listed.
Service License
Service licenses enable professional expertise provision including IT consultancy, legal advice, accounting, marketing, and business consulting. This category targets knowledge-based and professional service sectors.
The license supports both client-facing services and internal corporate functions such as regional headquarters operations. Many professional service providers choose this license when establishing freezone company formation in Dubai.
Industrial License
Industrial licenses support manufacturing, assembly, and packaging operations. This permit typically requires leasing Light Industrial Units (LIUs) to accommodate machinery and production lines.
The license is coupled with access to the DAFZ Industrial Park, which provides specialized infrastructure including high ceilings for storage, power capacity up to 200kW, and proximity to airport cargo facilities.
General Trading License
For businesses dealing in multiple unrelated product categories, the general trading license provides the broadest operational scope. DAFZA requires minimum share capital of AED 500,000 for this license type, reduced from the previous AED 1 million requirement.
This license offers maximum flexibility for diversified trading operations but carries higher capital requirements and enhanced regulatory scrutiny.
Specialized Modern Licenses
Dual License with DET: Developed with Dubai Department of Economy and Tourism, this innovative license allows DAFZA entities to operate on the mainland without establishing a separate legal entity. It maintains 100% foreign ownership while enabling direct local market access and participation in government tenders.
E-commerce License: Designed for online retailers, this license authorizes trading goods and services through digital platforms.
Talent Pass: Targeting individual freelancers in media, technology, and education sectors, this license includes a three-year residency visa and costs AED 9,500 annually.
Single/Multi-Family Office (SFO/MFO) Licenses: These specialized permits cater to wealthy families requiring wealth management, investment advisory, and estate planning services.
Complete Registration Process: Nine Essential Steps
The incorporation journey follows three broad phases—Choose, Submit, and Collect—encompassing nine detailed procedural steps. Understanding each stage prevents delays and ensures compliance.
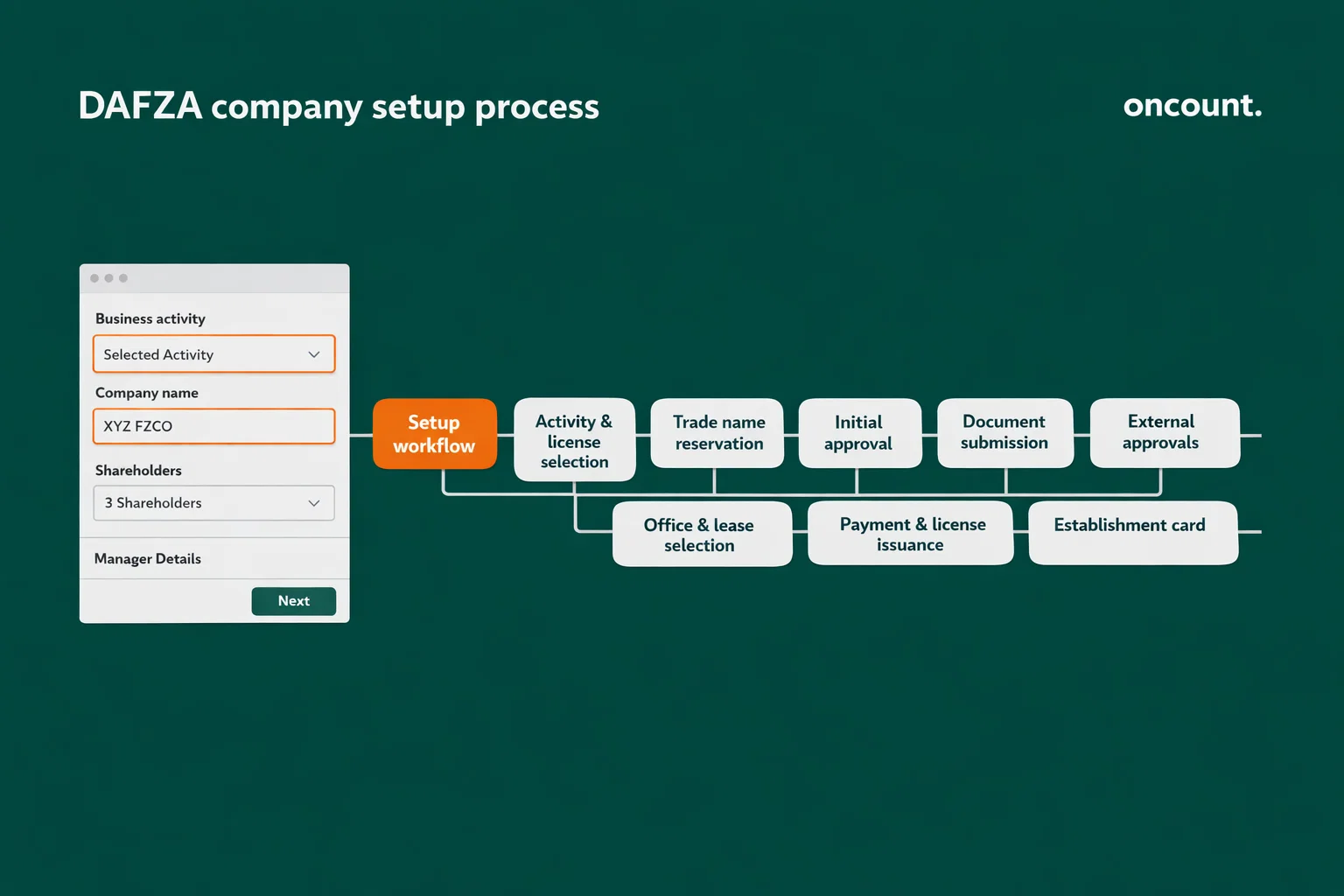
Step 1: Select Business Activity and License Type
Begin by identifying whether your business primarily engages in trading, services, or industrial operations. This determination dictates license type and required regulatory approvals.
DAFZA offers over 2,000 economic activities across 18 sectors. Regulated activities require additional permits from external government bodies before license issuance. Choosing activities carefully prevents scope limitations later.
Step 2: Reserve Your Trade Name
Propose a unique trade name to the authority. The name must not infringe intellectual property rights, violate public order, or contain restricted terms like “bank” or “insurance” without specific authorization.
The name must conclude with the legal suffix representing your company structure (FZCO, FZE, etc.). Name approval typically processes within 1-2 business days.
Step 3: Obtain Initial Approval
The DAFZ Authority reviews your proposed business model and shareholder profiles. If shareholders are UAE residents under different sponsorship, provide a No Objection Certificate (NOC) from the current sponsor.
This milestone confirms the authority’s acceptance of your business concept and shareholder structure. Initial approval is prerequisite for proceeding to documentation submission.
Step 4: Submit Formal Application Dossier
Compile a comprehensive file including passport copies of shareholders, directors, and appointed manager, along with curriculum vitae and personal bank reference letters.
For most license categories, include a brief business plan outlining objectives, target markets, financial projections, and management team backgrounds. Documentation quality directly impacts processing speed.
Step 5: Secure External Regulatory Approvals
If your activity falls under regulated sectors, obtain necessary clearances from relevant UAE ministries. DAFZA facilitates this process but cannot substitute for required ministerial approvals.
Common regulated sectors include healthcare, education, food and beverage, and financial services. Factor additional processing time (2-4 weeks) for external approvals.
Step 6: Select and Lease Office Space
UAE law requires every company to maintain a registered office address within the free zone. Choose from shared flexi-desks, private serviced offices, or expansive warehouses based on operational needs.
Signing the lease agreement is mandatory before license issuance. The lease also determines visa quota allocation, as visa entitlement correlates with office size.
Step 7: Settle Registration and License Fees
Upon finalizing all documentation and approvals, pay registration fees, annual license fees, and lease payments. DAFZA issues invoices through its online portal.
Payment completion triggers the final processing stage. Most investors receive their incorporation documents within 3-5 business days after full payment.
Step 8: Collect Incorporation Documents
DAFZA issues the Trade License, Certificate of Incorporation, Memorandum of Association (MOA), and Share Certificates. These documents establish legal existence and define shareholder rights.
The authority also provides an Establishment Card, which enables visa processing for employees. Safeguard these documents as they’re required for banking, visa applications, and regulatory compliance.
Step 9: Complete Visa Processing and Open Bank Account
Use the Establishment Card to initiate employment visa applications. The visa process involves entry permit issuance, medical fitness testing, Emirates ID registration, and final visa stamping.
Simultaneously, approach banks to open a corporate account. This process typically takes 2-4 weeks and requires comprehensive KYC documentation. Full operational capacity is achieved only after visa stamping and bank account activation.
Mandatory Documentation for Company Formation
Proper documentation preparation accelerates the incorporation process and prevents rejection. Documents must meet specific attestation and translation requirements.
Personal Documentation Requirements
For Individual Shareholders and Directors:
- Valid passport copies (minimum 6 months validity)
- Passport-size photographs (white background)
- Current residential address proof
- Personal bank reference letters (recent, from recognized banks)
- Curriculum vitae detailing professional background
UAE residents must provide Emirates ID copies and, if under existing sponsorship, a No Objection Certificate from the current sponsor.
Corporate Shareholder Documentation
For Companies Owning Shares:
- Certificate of Incorporation from origin country
- Memorandum and Articles of Association
- Board Resolution authorizing investment in UAE
- Certificate of Good Standing or equivalent
- Shareholder register and directors list
All corporate documents must be notarized, attested by the UAE Embassy in the origin country, and legalized by the UAE Ministry of Foreign Affairs. This attestation process can take 3-6 weeks depending on jurisdiction.
Supporting Business Documents
Additional Requirements:
- Detailed business plan (3-5 pages recommended)
- Financial projections for first 2-3 years
- Source of funds documentation for capital investment
- Professional reference letters (if applicable)
For branch offices, provide audited financial statements from the parent company for the last two fiscal years. Some regulated activities require professional certifications or industry-specific licenses.
Financial Investment Required for DAFZA Setup
Budget planning should account for both initial establishment costs and recurring annual expenses. DAFZA has implemented fee reductions up to 65% in recent years to support SMEs.
Initial Registration and License Fees
| Expense Category | Component | Estimated Cost (AED) |
| Registration | One-time Setup Fee | 5,000 – 10,000 |
| License | Annual Trade/Service License | 15,000 – 17,000 |
| General Trading | Additional Capital Requirement | 500,000 (share capital) |
License fees vary based on activity type and number of activities listed. Multiple activities on a single license may incur additional charges.
Immigration and Visa Costs
| Visa Service | Cost Range (AED) |
| Establishment Card (Annual) | 2,020 – 3,000 |
| Employment Visa (per person) | 4,000 – 6,000 |
| Visa Renewal (Annual) | 3,500 – 5,000 |
| Dependent Visa | 3,000 – 4,500 |
Visa allocations depend on office size. Smaller offices (Smart/Boutique) typically include 1-2 visas, while larger Premium Plus offices (50 sqm) accommodate up to 6 visas.
Office and Infrastructure Expenses
Annual Leasing Costs:
- Smart Office (6-10 sqm): AED 15,000 – 25,000
- Boutique Office (9-23 sqm): AED 25,000 – 35,000
- Premium Office (25 sqm): AED 40,000 – 60,000
- Premium Plus (50 sqm): AED 70,000 – 90,000
- Standard Office (25+ sqm): AED 80,000 – 150,000
Additional recurring fees include P.O. Box rental (AED 1,010 – 1,065 annually) and Knowledge & Innovation Fee (AED 60).
Total First-Year Investment Estimate
For a typical FZCO trading entity with a Premium Office (25 sqm) and two employment visas, expect a first-year investment between AED 90,000 and AED 110,000.
This estimate includes registration, license, office lease, visa processing, and administrative fees. Add mandatory office insurance and employee health insurance costs, which vary by provider.
DAFZA Free Zone vs UAE Mainland Company Comparison
Choosing between free zone and mainland structures requires understanding operational differences, market access limitations, and regulatory frameworks.
Ownership Structure Differences
Free Zone: 100% foreign ownership permitted without local partner or sponsor. Investors maintain complete control over equity, operations, and profit distribution.
Mainland: Most activities require 51% UAE national ownership, though recent reforms allow 100% foreign ownership for specific licensed activities. Local Service Agent (LSA) may be required for certain sectors.
Market Access and Trading Scope
Free Zone: Direct mainland trading is restricted without a Dual License or mainland distributor. Free zone companies primarily serve international markets and other free zones.
Mainland: Unrestricted access to UAE local market, ability to participate in government tenders, and direct trading with mainland entities. No geographical limitations within UAE.
Taxation and Financial Obligations
Free Zone: Potential 0% corporate tax on qualifying income if meeting “Qualifying Free Zone Person” criteria. VAT exemption for designated free zone transactions.
Mainland: Subject to 9% corporate tax on profits exceeding AED 375,000. Standard VAT obligations apply. Potential tax treaty benefits depending on business structure.
Office and Physical Presence Requirements
Free Zone: Must lease office space within the free zone. Flexi-desk options available for small operations starting around AED 15,000 annually.
Mainland: Must lease or own commercial space in mainland Dubai. Minimum office requirements vary by activity. Costs generally higher than free zone equivalents.
Regulatory Framework and Compliance
Free Zone: Governed by DAFZA regulations under Dubai Law No. 25 of 2009. Streamlined processes with most services available through single authority.
Mainland: Regulated by Department of Economy and Tourism (DET) and various government departments. More complex approval processes involving multiple authorities.
The Dual License option bridges this gap, allowing DAFZA entities to access mainland markets while maintaining free zone benefits—an ideal solution for service-based and consulting firms.
Ongoing Compliance and Regulatory Obligations
Maintaining good standing requires fulfilling continuous compliance requirements under both DAFZA regulations and UAE federal law.
VAT Registration and Filing
Companies with annual turnover exceeding AED 375,000 must register for VAT with the Federal Tax Authority. Registration is optional for turnover between AED 187,500 and AED 375,000.
VAT rate is 5% on most goods and services. Registered entities must file quarterly VAT returns and maintain detailed transaction records. Late filing incurs penalties starting at AED 1,000.
Corporate Tax Compliance
The UAE federal corporate tax of 9% applies to profits exceeding AED 375,000. DAFZA entities may qualify for 0% tax on “qualifying income” by meeting substance requirements.
To maintain tax exemption status, companies must:
- Conduct core income-generating activities within the free zone
- Maintain adequate qualified employees
- Demonstrate sufficient operational expenditure in UAE
- Avoid transactions designed primarily for tax avoidance
Economic Substance Regulations (ESR)
Companies engaged in “Relevant Activities” (banking, insurance, shipping, headquarters business, etc.) must file annual ESR notifications and reports with the Ministry of Finance.
ESR compliance requires demonstrating adequate employees, physical assets, and expenditure in UAE relative to the activity. Penalties for non-filing or inadequate substance can reach AED 50,000 or more.
Ultimate Beneficial Owner (UBO) Reporting
All DAFZA companies must maintain a UBO register identifying natural persons owning or controlling 25% or more of capital or voting rights.
Changes in ownership or management must be reported to DAFZ Authority within 14 days. Failure to maintain accurate UBO records results in administrative fines and potential license complications.
Annual Audit Requirements
DAFZA-registered companies must submit annual audited financial reports prepared by DAFZA-approved auditors. This requirement applies during license renewal.
Financial statements should follow International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS). Failure to provide audited accounts can delay or prevent license renewal and may trigger regulatory penalties.
AML/CFT Obligations
Companies must implement Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Countering the Financing of Terrorism (CFT) policies, particularly those in financial services, real estate, or dealing with high-value transactions.
Maintain customer due diligence records, report suspicious transactions to authorities, and conduct regular risk assessments. Non-compliance carries severe penalties including license suspension.
Frequent Pitfalls in Free Zone Company Formation
Understanding common mistakes helps investors avoid costly delays, regulatory penalties, and operational disruptions.
License Scope Errors
Mistake: Selecting insufficient activities on the trade license, requiring amendment later when expanding services or products.
Consequence: License amendments involve additional fees (AED 2,000 – 5,000) and processing time. Some banks may freeze accounts pending license updates.
Prevention: Thoroughly analyze your business model and include all potential activities from the outset. Consult with business setup advisors to identify commonly overlooked activities.
Banking Relationship Delays
Mistake: Underestimating bank account opening timeframes and KYC requirements, assuming immediate access to banking services post-incorporation.
Consequence: Operations stall without payment processing capability. Contracts may be delayed, and business opportunities lost. The banking process typically takes 2-4 weeks.
Prevention: Engage banks early, prepare comprehensive business plans and financial projections, and ensure shareholders have clean financial histories with proper source of wealth documentation.
Tax Status Misunderstanding
Mistake: Assuming automatic 0% corporate tax without understanding “Qualifying Free Zone Person” requirements or failing to maintain adequate substance.
Consequence: Unexpected 9% tax liability on profits exceeding AED 375,000. Retroactive tax assessments can create significant financial burdens.
Prevention: Work with tax advisors to structure operations meeting qualifying criteria. Maintain proper documentation of employees, expenditure, and core activities conducted within the free zone.
Inadequate Compliance Planning
Mistake: Neglecting ongoing obligations such as annual audits, ESR filings, UBO reporting, and VAT returns.
Consequence: Administrative penalties, license renewal complications, potential business suspension, and reputational damage. ESR penalties alone can reach AED 50,000.
Prevention: Establish compliance calendars, engage accounting firms familiar with UAE regulations, and budget for annual audit costs (AED 5,000 – 15,000 depending on complexity).
Benefits of Professional Business Setup Support
Engaging experienced business setup and accounting firms provides strategic advantages beyond simple administrative convenience.
Jurisdiction Selection Expertise
Professional advisors analyze your specific business model, target markets, and operational requirements to recommend the optimal free zone or mainland structure.
They compare multiple jurisdictions based on licensing costs, visa allocations, market access, and industry-specific advantages—preventing costly jurisdiction mistakes that require restructuring later.
Documentation and Process Management
Experts ensure all documents meet attestation, translation, and legalization requirements before submission. This attention to detail prevents application rejections and processing delays.
They manage timelines, coordinate with multiple government departments, and maintain momentum through the 9-step incorporation process, typically completing setup 30-40% faster than self-managed applications.
Regulatory Compliance Framework
Professional firms establish proper compliance systems from day one, including accounting software setup, bookkeeping procedures aligned with IFRS, and compliance calendars for VAT, corporate tax, and ESR obligations.
They provide ongoing support for annual audits, tax filings, and regulatory reporting—reducing the risk of penalties and maintaining your company’s good standing with authorities.
Banking Relationship Facilitation
Established firms leverage existing relationships with UAE banks to streamline account opening processes. They prepare comprehensive KYC packages that meet banking requirements, reducing rejection rates and processing delays.
Their expertise in presenting business models to risk-averse banks increases approval probability, particularly for non-resident shareholders or novel business concepts.
Cost Optimization Strategies
While professional services involve fees (typically AED 8,000 – 20,000 for standard setups), they often identify cost savings through:
- Appropriate license selection avoiding over-specification
- Right-sized office packages matching actual needs
- Visa optimization strategies
- Package deals and promotional pricing awareness
The net result is often lower total cost than self-managed setups that incur amendment fees, penalties, and operational delays.