Understanding Audit Types Purpose Roles
For any entity operating in the UAE, the requirement for an audit is generally categorized by who mandates it, who performs it, and who the primary audience is. Clarifying the difference between internal review and other forms of inspection is the first step toward building a robust governance framework.
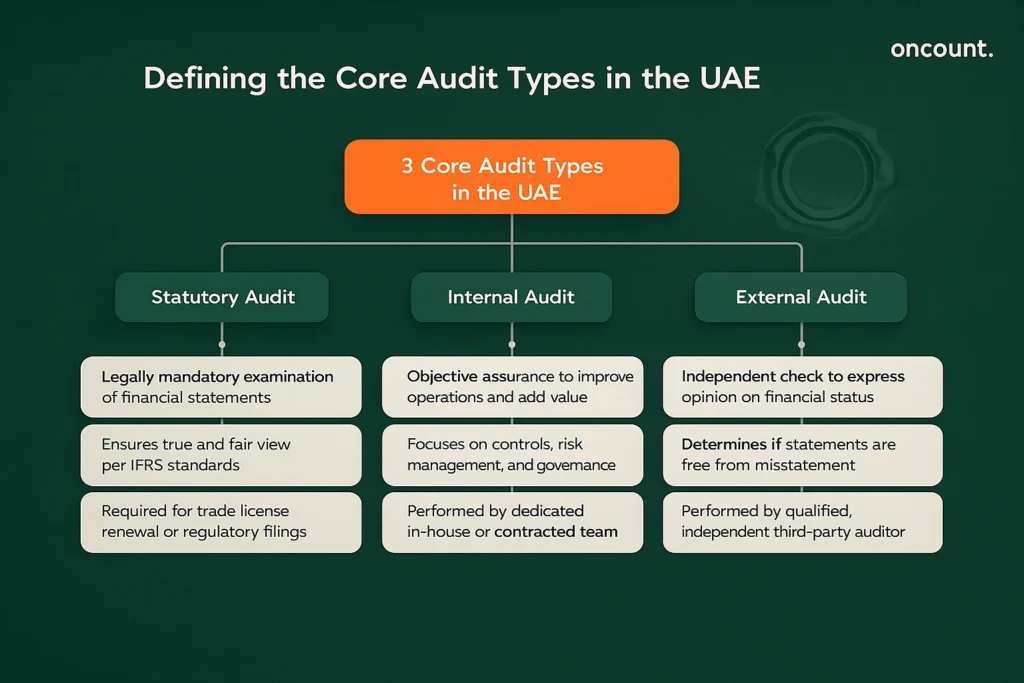
Statutory Audit Definition
A statutory audit is an independent, mandatory examination of a company’s company’s financial statements conducted to determine if they present a true and fair view in accordance with a specified financial reporting framework, such as IFRS as adopted in the UAE. This inspection is a legally required process for most mainland entities and is often necessary for trade license renewal or specific regulatory filings.
Internal Audit Definition
An internal audit is an independent, objective assurance and consulting activity designed to add value and improve an organization’s operations. The purpose of this function is not primarily focused on financial reporting accuracy, but on evaluating and improving the effectiveness of company controls, risk management, and governance processes. The internal review is conducted by the internal audit department or a dedicated company team.
External Audit Definition
An external audit is an independent examination of the company’s financial statements to express an opinion on whether they are free from material misstatement. It is conducted by a qualified, independent third-party auditor from an approved review firm registered with the Ministry of Economy (MoEc) in the UAE. The external verification provides credibility to financial data for external stakeholders.
Core Purpose Each Audit
While all types of reviews contribute to assurance, they serve distinct purposes. The statutory review ensures public trust and legal compliance; the external inspection validates financial transparency; and the company review focuses on operational efficiency and risk mitigation within the company’s own environment.
Internal Audit Key Features Purpose of Internal Audit
The internal audit function is a proactive management tool designed to protect and enhance value. It is often the first line of defense against operational failures and non-compliance with company policies.
Objectives Internal Audits
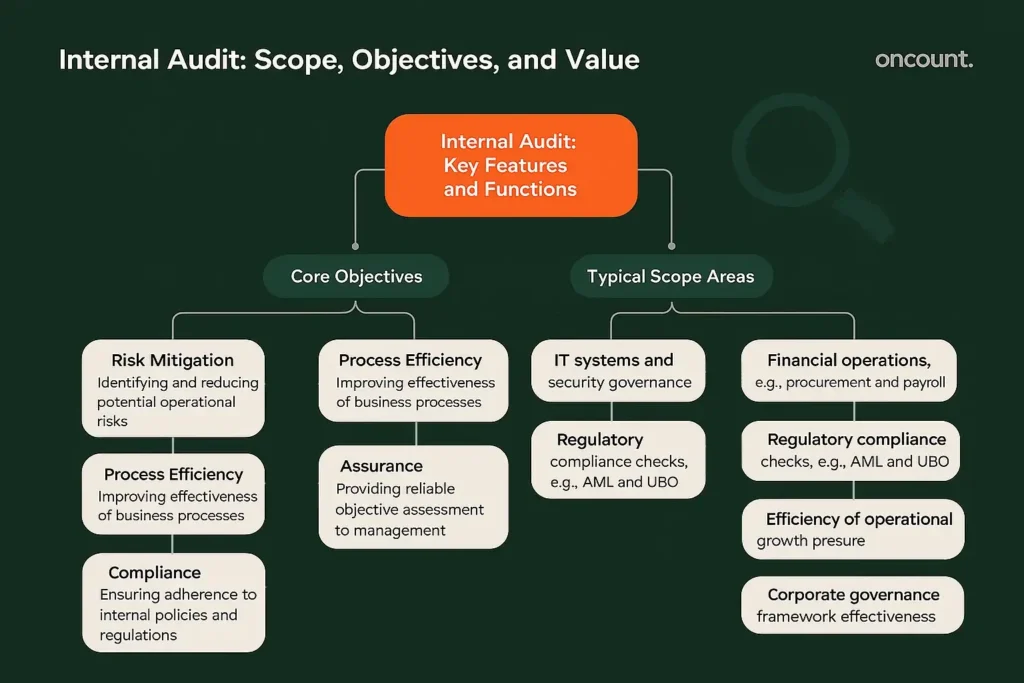
The goal of an internal review is to evaluate the effectiveness of company controls and ensure that the risk management systems are functioning optimally. Internal reviews serve to provide management and the board with an objective assessment of the organization’s health, focusing on the following core objectives:
- Risk Mitigation: Identifying and reducing potential risks (operational, financial, and compliance).
- Process Efficiency: Improving the effectiveness and efficiency of business processes.
- Assurance: Providing reliable assurance to management regarding controls and governance.
- Compliance: Ensuring adherence to internal policies, procedures, and external regulations.
Scope Internal Audits
The scope is dynamic and broad. Company reviews focus on processes across the entire business, including IT governance, efficiency, regulatory adherence, and the safeguarding of assets. For entities preparing for Corporate Tax, the internal auditor may specifically review data integrity and source documentation. The scope typically covers areas such as:
- IT systems and security
- Financial operations (e.g., procurement, payroll)
- Regulatory compliance checks (e.g., AML, UBO)
- Efficiency of operational processes
- Corporate governance framework
Frequency Conduct Internal Audits
The frequency is not legally mandated but is determined by the board or the review department based on risk. High-risk areas or critical functions (like payroll or procurement) may require an internal check quarterly, while others are reviewed annually as part of a detailed review plan.
Reporting Internal Audits
Company teams provide reports primarily to the board, the audit committee, and senior management. These reports contain detailed findings, risks, and actionable recommendations for company improvements to strengthen the control systems.
Internal Auditing Focus Operational Efficiency Risk Management
Internal reviews help management identify blind spots and process inefficiencies. By assessing company controls, the audit team ensures that the organization’s control systems are adequate to mitigate business risks.
Evaluating Internal Controls Governance
A critical function involves evaluating the effectiveness of these control systems, which encompasses the overall corporate governance structure, ethical compliance, and adherence to company policies.
External Audit Key Features Purpose of External Audit
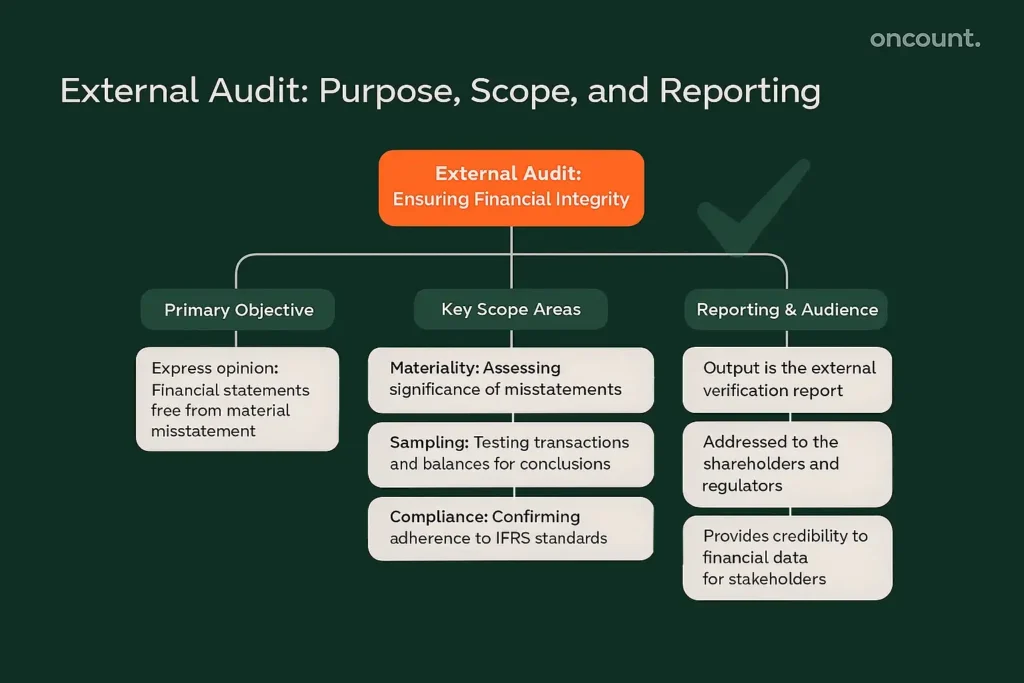
The external audit is focused on providing assurance to parties outside the company, ensuring trust in capital markets and the wider economy. The independent inspection is an attestation of the company’s financial integrity.
Objectives External Audits
The purpose of this review is primarily to express an opinion on whether the financial statements are accurate and free from material misstatement. This review ensures that the financial reporting is compliant with relevant accounting standards.
Scope External Audits
The scope is concentrated on the reliability of the company’s financial statements and the related control systems over financial reporting. The independent external auditor focuses on transactional completeness and valuation. Key areas of focus for the external auditor are:
- Materiality: Assessing the significance of misstatements in the financial statements.
- Sampling: Testing a selection of transactions and balances to draw conclusions.
- Compliance: Confirming adherence to IFRS and other statutory financial reporting requirements.
Frequency Conducting an External Audit
The external review is conducted annually, as mandated by regulatory and statutory requirements for most companies in the UAE.
Reporting External Audits
The output is the external verification report, which is addressed to the shareholders and often submitted to government agencies like free zone authorities or the MoEc. This review report is publicly accessible to external stakeholders.
External Auditing Independent Verification Financial Transparency
Independent reviews are essential because the independent nature of the external auditor provides an unbiased assessment, which is vital for securing investment, bank financing, and fulfilling compliance obligations.
Building Stakeholder Confidence
The positive external audit report provides assurance to investors, creditors, and government regulators that the reported financial position is trustworthy.
Statutory Audit Key Features Importance
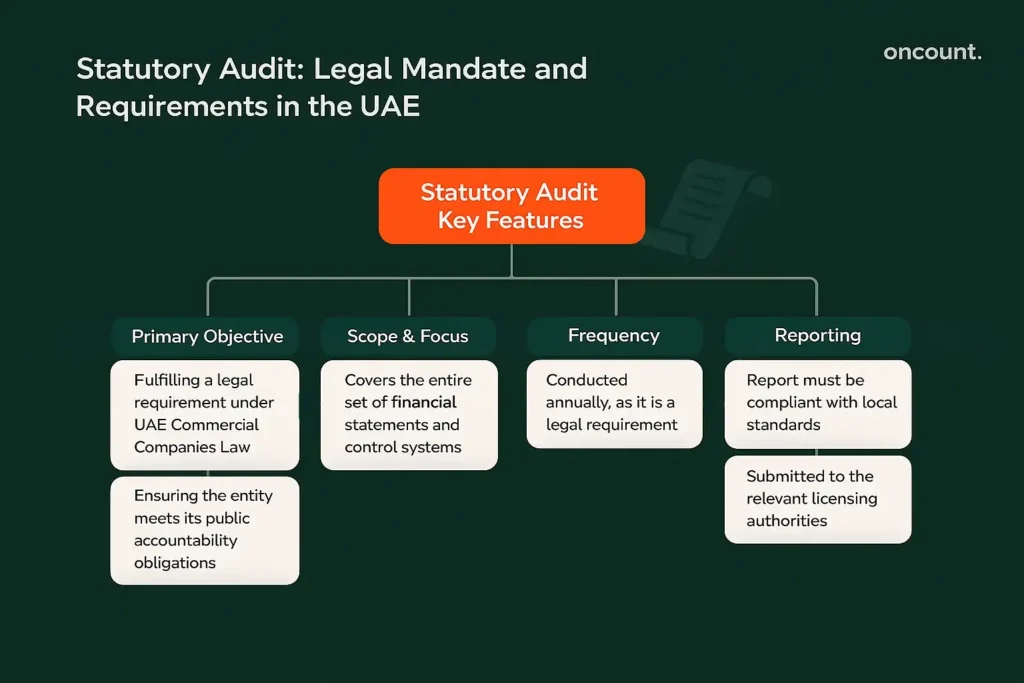
In the UAE context, the statutory audit often overlaps with the external review, as both are mandated by law and conducted by the independent auditor. However, the legal impetus is key.
Objectives Statutory Audits
The primary objective is fulfilling a legal requirement under the UAE Commercial Companies Law (Federal Decree Law No. 32 of 2021) and various free zone regulations. The review is legally required to ensure that the entity has met its public accountability obligations.
Scope Statutory Audits
The scope is defined by legal requirements and typically covers the entire set of financial statements and control systems over financial reporting.
Frequency Statutory Audits
As it is a legal requirement, the statutory inspection is conducted annually.
Reporting Statutory Audits
The review report must be compliant with local reporting standards and submitted to the relevant licensing authorities.
Ensuring Regulatory Compliance Accuracy
The statutory audit is indispensable in ensuring that a business operating in the UAE adheres to all necessary financial reporting regulations, including specific free zone requirements.
Legal Mandate Requirements
The requirement for a statutory review distinguishes it from an optional company function, making it a prerequisite for many business operations and renewals in the Emirates.
Key Differences: Internal Audit vs Statutory Audit
Clarifying the difference between internal review and statutory audit is critical for resource allocation and governance planning.
Appointment Authority Internal Statutory Auditors
The internal auditor or company team is appointed by the board or senior management. Unlike independent reviews, the statutory auditors are third-party professionals appointed by the shareholders (Owners) at the annual general meeting.
Who Performs Internal Statutory Audit
The internal review is conducted by employees of the company or a third-party service provider under a consultancy contract. The statutory inspection is conducted by an independent external auditor from a registered audit firm.
Stakeholder Audience Internal Statutory Reports
Own reports are for company use (management, board, review department). Statutory reports are for third-party stakeholders (shareholders, regulators, public registries).
Mandatory Nature Internal Statutory Audits
A statutory inspection is legally mandatory for most companies. The internal review is voluntary, though highly recommended, and may be mandated by a large parent company or specific regulatory bodies for certain sectors (e.g., financial services).
Internal Audit and Statutory Audit Comparative
The core distinctions between these two critical functions are summarized below:
| Feature | Internal Review | Statutory Audit |
| Mandate | Voluntary (Management/Board Decision) | Mandatory (Legal Requirement) |
| Focus | Risk Management, Efficiency, Governance | Financial Statement Accuracy, Law Compliance |
| Auditor | Employee or Contracted Consultant | Independent Third-Party Appointed by Shareholders |
| Audience | Management, Board, Audit Committee | Shareholders, Regulators, Public |
| Period | Ongoing, Flexible (e.g., quarterly, continuous) | Annual, Defined by Reporting Period |
Key Differences: Internal and External Audits (Internal vs External)
The core key differences between company reviews vs independent reviews revolve around independence and objective.
Internal Auditor vs External Auditor Independence Status
The external auditor maintains total independence from the company being audited; their opinion must be unbiased. The internal reviewer is an employee or a company team member, meaning they serve the company’s internal needs, although they must remain objective in their reporting.
Internal External Audit Focus Areas
Own reviews focus on operations, IT, ethics, and fraud prevention. The independent inspection focuses on financial reporting and ensuring the financial statements are accurate.
Who Needs Internal or External Audit
Every company legally required to submit financials needs an external review in UAE. The internal function is needed by companies seeking better governance, risk management, and operational improvements.
Internal External Audit Benefits
The advantages of company reviews include efficiency gains and better risk management. The external verification provides assurance and facilitates access to capital.
Key Differences: Statutory vs External Audit
In the UAE, the statutory audit is essentially the legal requirement that makes the external review necessary. The terms are often used interchangeably to refer to the mandatory financial statement review.
Statutory External Audit Similarities
Both are conducted by a third-party independent auditor and result in an external review report on the company’s financial condition. Both auditors must comply with ISA (International Standards on Auditing).
Statutory External Audit Overlap
The review serves to fulfil the same primary goal: validating the company’s financial statements. The distinction is often semantic, referencing either the legal reason (Statutory) or the nature of the service (External).
Distinct Roles Statutory External Auditors
While the function is the same, the statutory auditors review company documents with a view toward compliance with the Companies Law, while the independent auditor title emphasizes the independence element for third-party stakeholders.
Choosing Between Audit Types
Deciding whether to conduct company reviews or rely solely on external compliance depends on the company’s complexity, regulatory exposure, and growth stage.
When Conduct Statutory Audit
A statutory review is non-negotiable and inspection is carried out annually as per the law. This review is crucial for all license renewals, particularly in Dubai mainland and many free zones.
When Conduct Internal Audit
An internal review should be initiated when the organization grows in complexity, requires greater oversight, or is preparing for a major regulatory change (like Corporate Tax implementation) to evaluate the effectiveness of company processes.
How Choose Internal External Audit
It’s not a choice of “internal or external” but rather “company and independent.” A well-managed firm uses the work of the company reviewer to smooth the review process and reduce risks identified by the external verification.
Audit Similarities Key Takeaways
Despite the key differences, the fundamental goal of any review remains consistent: transparency and trust.
Common Audit Objectives
All three review types share the objective of promoting accuracy and integrity in corporate processes, ensuring accountability, and ultimately preserving the company’s reputation. These shared goals include:
- Accountability: Ensuring that management is responsible for financial and operational outcomes.
- Integrity: Verifying the reliability and completeness of information and systems.
- Risk Mitigation: Identifying areas where failure could cause significant loss or harm.
Audit Procedures Involvement
The review process in all cases involves the gathering of evidence, detailed reviews, and following an established review plan to test controls and balances. The review procedures require significant input from the finance and operations team. Typical procedures involve:
- Inspecting documentation (invoices, contracts).
- Observing physical processes and control performance.
- Confirming balances with third parties (banks, customers).
- Reperforming calculations and reconciliations.
- Analyzing variances and trends in data.
Value Audits Organizations
Regardless of the type, every review adds value. The difference between company and independent value is that the former delivers operational value, while the latter delivers stakeholder assurance.