IFRS Regulatory Framework in the UAE Context
The regulatory landscape in the UAE requires a clear understanding of the entities driving the implementation and enforcement of international accounting requirements.
Governing Bodies and Influence on International Accounting Standards
The adoption of these standards is primarily governed by the UAE’s Ministry of Finance (MoF). However, enforcement and specific reporting requirements are handled by multiple entities. The Securities and Commodities Authority (SCA) mandates the compliance of publicly listed companies on exchanges like the Dubai Financial Market (DFM) and the Abu Dhabi Securities Exchange with Full international financial reporting standards regulations. These public companies operating in the UAE must align their reporting practices directly with the frameworks published by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB). This multi-layered oversight reinforces the commitment to transparent financial reporting across the Emirates.
Key Legislation and Mandates for IFRS
The foundation of modern reporting principles in the UAE is the mandate to comply with these standards. The UAE has adopted the IFRS framework as the required standard for many entities. This approach simplifies cross-border transactions and enhances the comparability of financial statements. Key compliance objectives under UAE law include:
- Ensuring the company’s statements present a true position.
- Making reports reliable for stakeholders, banks, and the Federal Tax Authority (FTA).
- Avoiding severe administrative fines, as failure to maintain accurate records based on this robust framework can result in a significant penalty under the respective regulatory body’s mandates.
IFRS Adoption for Mainland and Free Zone Companies in the UAE
While the UAE has adopted IFRS broadly, the specific application can vary between jurisdictions. Mainland companies, governed by commercial company law, are generally expected to use the international financial reporting standards provisions for reporting purposes. For businesses operating in Dubai and other Emirates’ free zones, the license issuing authority often specifies IFRS as the mandatory requirement. Crucially, with the introduction of Corporate Taxation, all Taxable Persons (including those operating in the UAE free zones seeking preferential rates) are required to calculate their taxable income starting from standards-compliant accounts, making this an absolute necessity for compliance regardless of location within the UAE.
IFRS Application and Accepted Accounting Standards
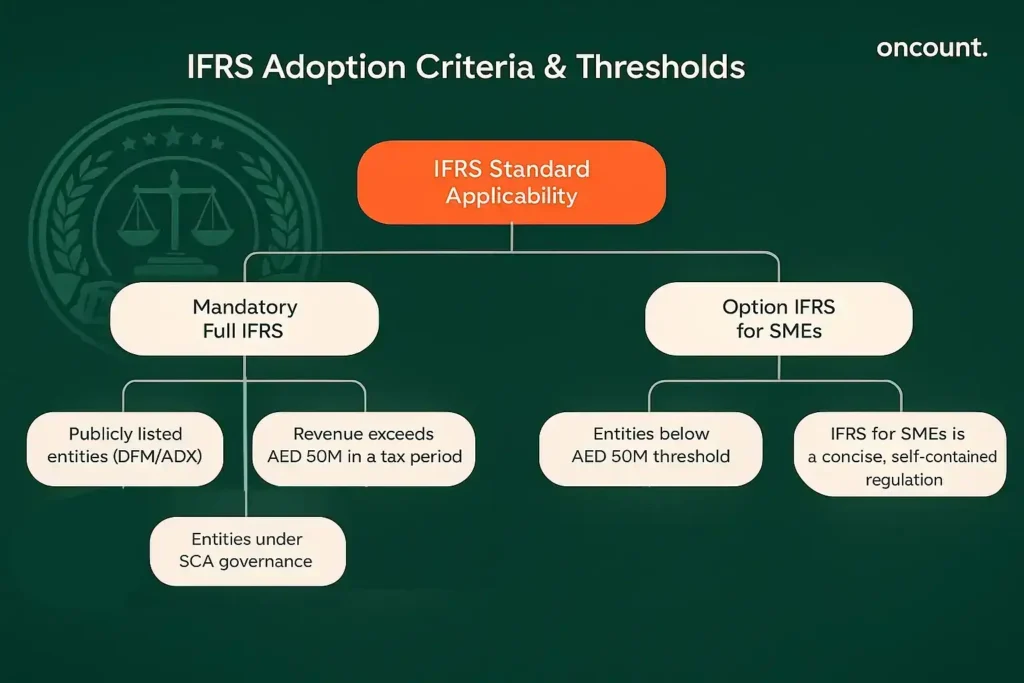
The international financial reporting standards principles are not a monolithic set of rules; the UAE permits flexibility based on the size and nature of the business.
Full IFRS vs. IFRS for SMEs
The primary distinction in practices centers on the size of the entity. While small and medium-sized entities may utilize the simpler IFRS for SMEs (a concise, self-contained version of the full standard), Full IFRS provisions (including all IAS and framework standards) are mandatory for:
- Publicly listed entities (e.g., on DFM, ADX).
- Taxable Persons deriving revenue exceeding AED 50 million in a Tax Period.
- Entities governed by the Securities and Commodities Authority (SCA).
Entities below the AED 50 million threshold have the option to use IFRS for SMEs, simplifying their reporting burden while still adhering to an internationally recognized standard.
Accounting Method and Principles
IFRS mandates the accrual method as its foundation. Under this principle, revenue is recognized when goods are delivered or services are rendered, and expenses are recognized when they are incurred, irrespective of whether cash is exchanged. This ensures the company’s statements accurately reflect the economic activities during the period, providing superior comparability and a better reflection of the true financial position. This accrual basis principle is essential for all entities preparing their core statements under the IFRS body of rules.
Generally Accepted Accounting Standards (GAAP) Context
While international financial reporting standards is the mandated standard for statutory reporting in the UAE, the term Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) is sometimes used informally or in reference to historical or localized reporting practices. It is critical to understand that for the most authoritative reporting—specifically for tax purposes and public disclosure—the accepted reporting standards in the UAE are defined as the IFRS requirement or IFRS for SMEs. Businesses must ensure their internal and tax records align with the strict requirements of IFRS to prevent reconciliation issues during an external audit.
IFRS and UAE Corporate Tax
The new UAE Corporate Tax regime fundamentally linked the taxable base to the IFRS-reported net profit, making international financial reporting standards compliance non-negotiable for tax purposes.
Financial Statements for Tax Groups
The UAE Corporate Tax Law contains specific tax provisions for Tax Groups. Instead of individual returns, a Tax Group must file a single consolidated return. For Tax Periods commencing on or after 1 January 2025, Ministerial Decision No. 84 of 2025 mandates that all Tax Groups must prepare and maintain audited Special Purpose Financial Statements (SPFS) based on an aggregation of the standalone IFRS financials of all group members. This specialized report is essential for determining the aggregated taxable income and ensuring proper elimination of intra-group transactions.
Calculating Taxable Income from IFRS Net Profit
Determining the final taxable income is a two-step process that starts with the financial results generated by IFRS:
- Determine Reported Net Profit: Calculate the net profit based on Standards-compliant statements.
- Apply Tax Adjustments: Subject the Net Profit to mandatory additions (e.g., non-deductible expenses like certain fines) and subtractions (e.g., exempt income such as qualified participation dividends) as specified by the tax laws.
It is the specialized role of the accountant to accurately navigate these adjustments, ensuring the final tax computation adheres strictly to the tax regulations and the IFRS reporting requirements used as the starting point.
Accrual vs. Cash Basis Accounting Method for Tax Purposes
While IFRS mandates the accrual basis for the core statements, the UAE Corporate Tax law provides flexibility for smaller entities. Taxable Persons whose revenue does not exceed AED 3 million may elect to use the simpler cash principle for calculating their taxable income. Under this system, income is recognized only when cash is received or paid, simplifying bookkeeping. However, this is an election for tax purposes only; the underlying records for statutory reporting may still need to maintain a separate reporting method.
Financial Reporting, Audit, and Accounting Services

Rigorous reporting and external audit are cornerstone requirements that ensure the integrity of a company’s financial data for regulators and stakeholders.
Mandatory Financial Reporting Requirements and Compliance
All Taxable Persons within the UAE must maintain accurate and transparent records and supporting documentation for a minimum period of five years. This requirement is paramount for compliance. Beyond simple bookkeeping, entities must maintain their records in a manner that allows for the easy preparation of IFRS-compliant statements. Software capable of managing complex transactions and supporting the accrual basis principle is a necessary tool for businesses to comply with the international financial reporting standards framework efficiently.
Audit and Assurance Services in the UAE
The requirement for an independent audit has been significantly tightened under the new tax laws. Audited statements are now mandatory for businesses if their annual revenue exceeds AED 50 million or if they are a Qualifying Free Zone Person, irrespective of their revenue. The independent auditor provides assurance that the company’s financial statements are free from material misstatement and prepared in accordance with IFRS guidelines. Professional services offer comprehensive accounting services including assistance with the valuation and application of complex IFRS such as those related to financial instruments.
Components of IFRS Financial Statements
The IFRS framework specifies that a complete set of statements must include five integrated components:
- A Statement of Financial Position (Balance Sheet).
- A Statement of Profit or Loss and Other Comprehensive Income.
- A Statement of Changes in Equity.
- A Statement of Cash Flows.
- Notes, comprising a summary of significant accounting policies and other explanatory notes.
These components collectively offer the comparability of financial statements that is vital for investors looking at entities listed on the Nasdaq Dubai or other regulated markets.
IFRS Compliance and Enforcement
Case Studies of Non-Compliance Consequences
Non-compliance with IFRS and associated tax laws can lead to severe consequences. For instance, a small trading firm in Dubai that failed to maintain sufficient records was recently subject to an AED 10,000 fine for inadequate bookkeeping, which doubled upon a repeat violation. Furthermore, using a non-compliant reporting method can lead to an inaccurate calculation of taxable income, resulting in penalties based on the under-declared tax amount. For listed companies, reporting violations can lead to suspension by the Securities and Commodities Authority (SCA).
Recommendations for Businesses and the Role of the Accountant
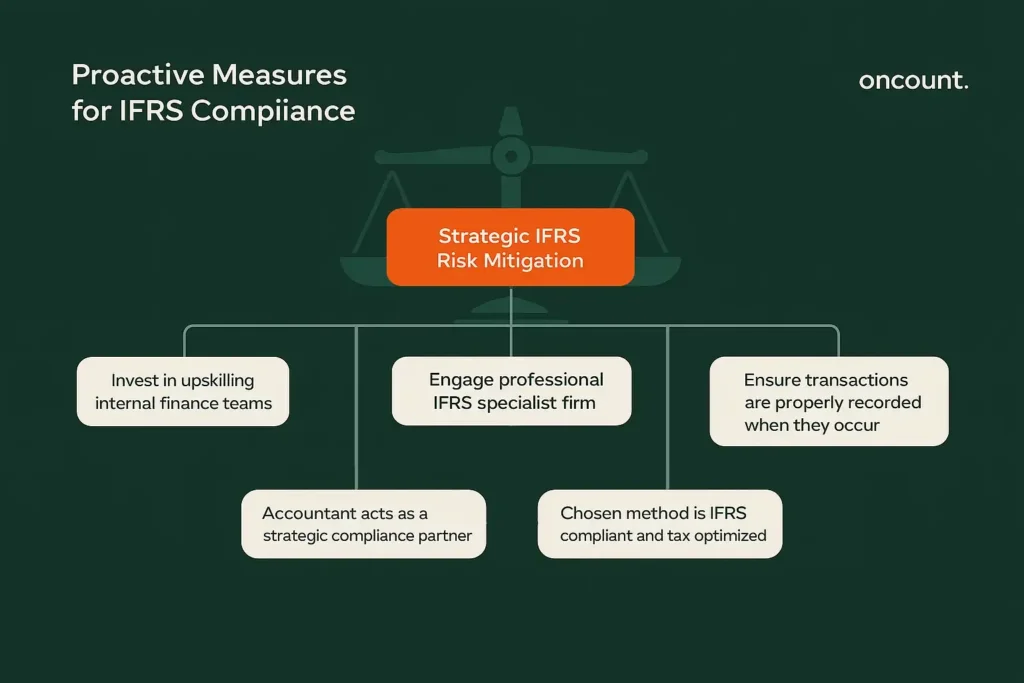
To mitigate risk, businesses must prioritize proactive measures to comply with IFRS. It is crucial for businesses to invest in upskilling their finance teams or engaging a professional accountant or firm specializing in IFRS provisions in Dubai. The accountant is no longer just a bookkeeper but a strategic partner who ensures all transactions are properly recorded when they occur, and that the chosen method is both international financial reporting standards compliant and optimized for tax purposes. Regular internal reviews and mock audits are highly recommended.
Transition Planning Tips Regarding New Tax Laws
The introduction of tax laws necessitates a review of internal systems. Effective transition planning is key to mitigating compliance risk:
- Review Basis of Accounting: Transition fully to the accrual basis if the cash basis was previously used (unless you qualify for the AED 3 million exception).
- Update Fixed Asset Registers: Ensure depreciation and amortization calculations align with international financial reporting standards requirements for accurate asset valuation.
- Coordinate Audit Schedules: Understand that the audit requirement for those exceeding AED 50 million in revenue is now directly tied to the tax return submission, demanding seamless coordination between the finance team and the external auditor.